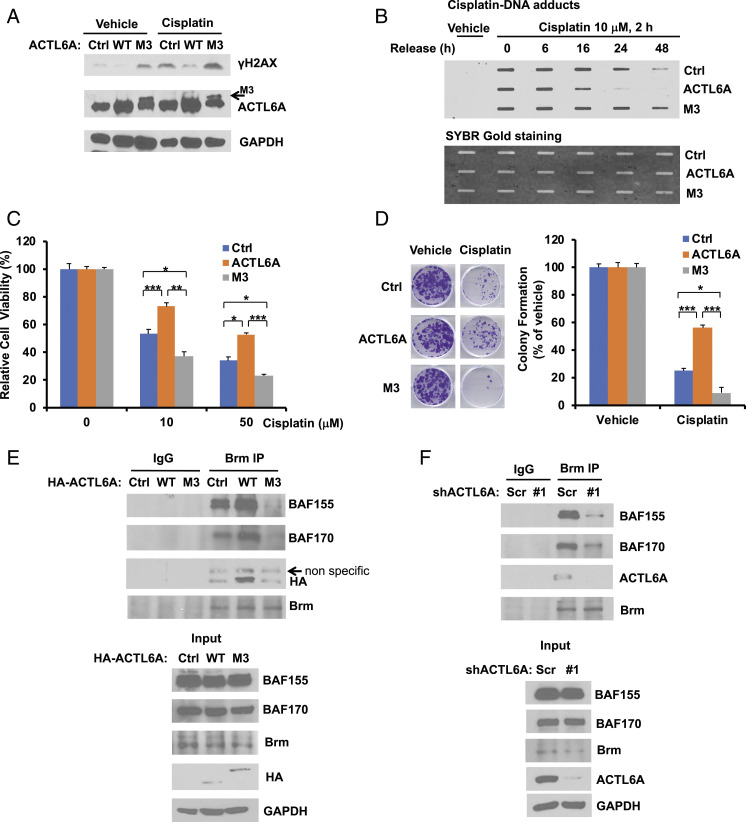
Fig. 6.
The ACTL6A mutant defective in Brg1 binding promotes the H2AX activity and cisplatin sensitivity by blocking DNA repair and the recruitment of the SWI/SNF complex. (A and B) In contrast to wild-type ACTL6A, the M3 mutant of ACTL6A, which is impaired in Brg1 binding, enhances H2AX activation and inhibits the repair of cisplatin-DNA adducts. H1299 cells stably overexpressing an empty vector (Ctrl), wild-type (WT) ACTL6A, or the M3 mutant of ACTL6A were treated with vehicle (PBS) or 10 μM cisplatin for 24 h (A) or 2 h (B). The activation of H2AX was determined by Western blot analysis (A). The slot blot assay was performed to determine the repair of cisplatin-DNA adducts (B). (C and D) Overexpression of the M3 mutant of ACTL6A enhances cisplatin sensitivity. Stable H1299 cells as indicated were treated with cisplatin, followed by MTT cell viability assay (C) or clonogenic cell survival assay (D) as described in Fig. 2 A and B, respectively. For cell viability assay (C), data shown represent the mean ± SD from at least three or four biological replicates. For colony formation assay (D), data shown represent the mean ± SD from at least three independent experiments. Representative images are shown on the Left of each figure. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. (E) Wild-type ACTL6A binds to Brm and promotes the recruitment of both BAF155 and BAF170 to Brm, whereas the M3 mutant of ACTL6A blocks this complex formation. H1299 cells stably overexpressing an empty vector (Ctrl) or HA-tagged ACTL6A (WT or M3 mutant) were harvested for coimmunoprecipitation. Endogenous Brm was immunoprecipitated with an anti-Brm rabbit monoclonal antibody or a control rabbit IgG, followed by immunoblotting. (F) Depletion of ACTL6A impairs the recruitment of both BAF155 and BAF170 to the Brm complex. H1299 cells stably expressing shScr or shACTL6A were harvested, and the endogenous protein coimmunoprecipitation of Brm with BAF155, BAF170, or ACTL6A was performed as described in E.