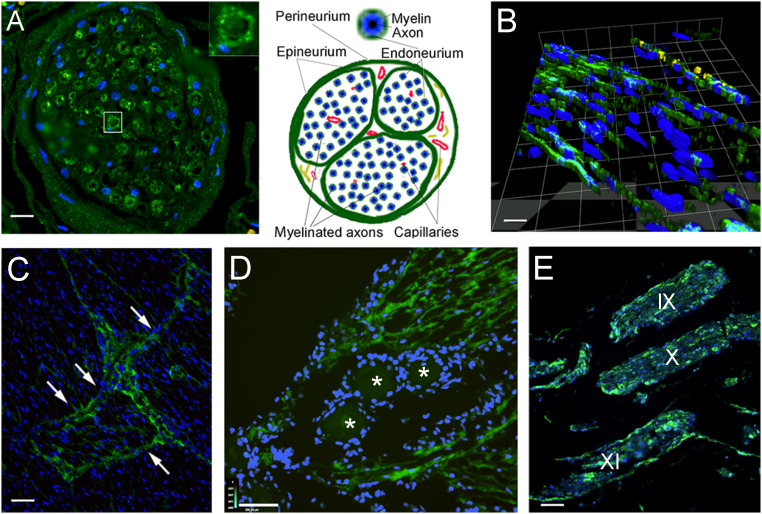
Fig. 5.
Lymphatic endothelial markers among the nerve fibers and fascicles of cranial nerves. Sections stained with antibody to LYVE1 (visualized in green fluorescence) of cranial nerves and the trigeminal ganglion from persons deceased without known neurological disorders. (A) Cross-sections of a branch of the trigeminal nerve are shown. Interestingly, the endoneurium (connective tissue sheets around the individual myelinated fibers) is positively stained; the Inset shows an enlargement of a single nerve fiber enclosed by the LYVE1-positive endoneurium. Nuclei of glial cells (Schwann cells and possibly microglia) and connective tissue are visible in blue (DAPI). In B, a three-dimensional reconstruction of a section of the trigeminal nerve is shown, demonstrating the presence of longitudinal LMPCs among the nerve fibers. On the Top of the image, cells with yellow fluorescence express the von Willebrand factor, indicating vascular endothelial cells of a small vessel in the section. (C) In a cross-section across a large nerve bundle, labeling is very strong among the fascicles (arrows). (D) A section through the trigeminal ganglion is shown. Cross-sections of trigeminal fibers around the ganglion cells (labeled with stars) show strong LYVE1 labeling. (E) Section of the brainstem with the origin of the IX, X, and XI cranial nerves running parallel. The perineurium as well as cells among the myelinated axons within the nerve fibers are strongly labeled with LYVE1. (Scale bars: A, 50 μm; B, 25 μm; C and E, 110 μm; D, 130 μm.)