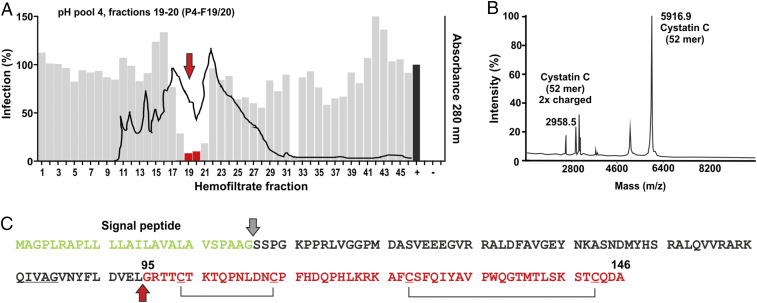
Fig. 1.
Identification of a C-terminal cystatin C fragment inhibiting GPR15-mediated SIVmac infection. (A) The gray bars indicate the efficiency of SIVmac239 infection of GHOST-GPR15 cells in the presence of the hemofiltrate peptide library fractions compared to the absence of peptide (100%), and the black line indicates the peptide/protein elution profile. Fractions used for further peptide purification are indicated in red and highlighted by an arrow. + indicates infection in the absence of peptide; − shows uninfected cells. (B) MALDI-TOF spectrum of the active fraction obtained after the fifth round of purification. Sequence analyses identified the 52 C-terminal residues of cystatin C. (C) Amino acid sequence of human cystatin C. The signal peptide (green), the isolated peptide (red), and putative C-C bridges are indicated. The cleavage site to generate CysC95-146 is indicated by a red arrow.