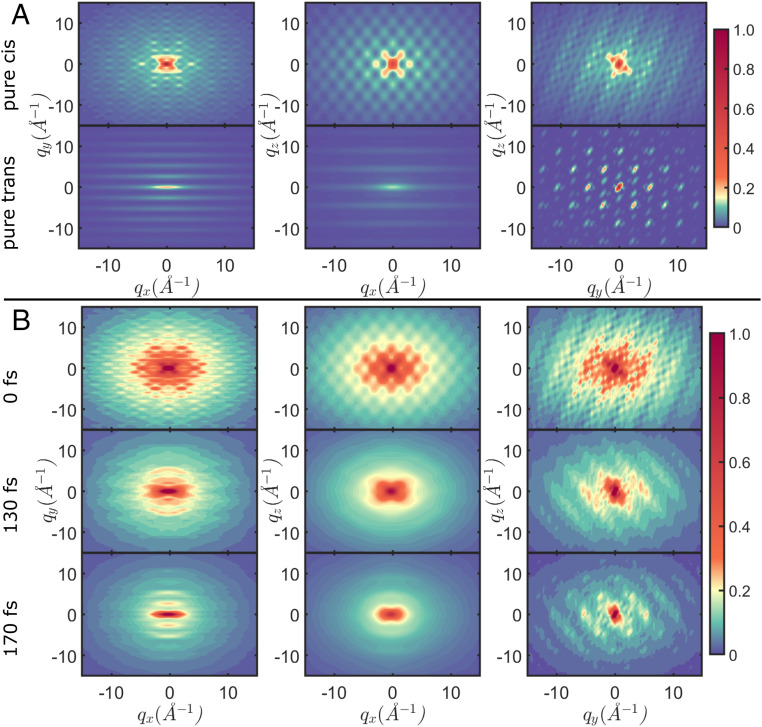
Fig. 4.
Two-dimensional diffraction patterns of the total signal (Eq. 3) in the , , and planes, while integrating over the respective other direction. The molecular axes are defined in Fig. 1(A. (A) Scattering from the pure cis (Top) and trans (Bottom) geometry. This is not observable, since spread of the nuclear wave packet is not accounted for, but serves as a reference. (B) Diffraction patterns at 0, 130, and 170 fs during the dynamics. The pattern at 0 fs resembles the pure cis geometry in A. A change in pattern is observed at 130 fs, where parts of the wave packet have passed the CoIn. At 170 fs, where a considerable amount of the wave packet has reached the product minimum, the diffraction pattern includes features from the pure trans pattern in A. The isomerization can be followed in real time. The complete movie is provided as electronic supplement (Movie S3).