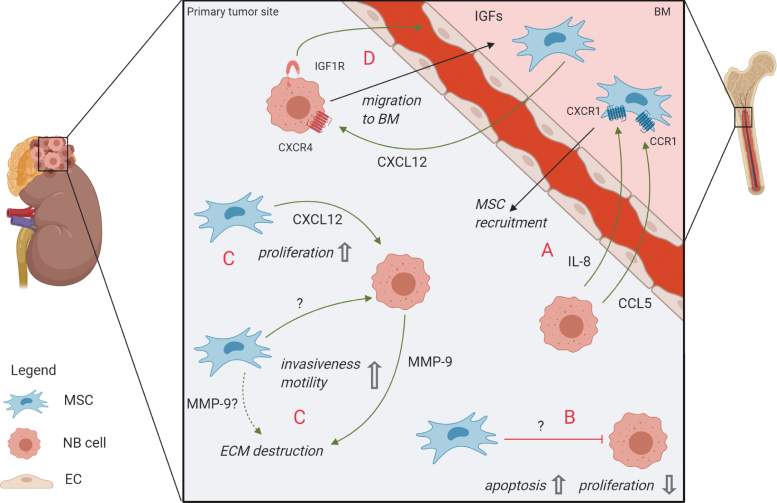
FIG. 1.
Crosstalk between MSCs and NB cells at the primary tumor site and migration to/from the BM. (A) MSCs are attracted from the BM to the primary site (among others through CXCR1/IL-8 and CCR1/CCL5 signaling) [52]. (B) Unknown MSC-derived mediators can exert a tumor-suppressive effect [68]. (C) The CXCR4/CXCL12 axis plays a role in proliferation and survival of tumor cells and decreased apoptosis rates [74]. MMP-9 [99,100] might play a role in promoting EMT and metastasis: unknown signaling events from MSCs induce MMP-9 expression in NB cells [100], whereas MSCs potentially also secrete MMP-9 themselves (dashed line). (D) NB cells are attracted to the BM metastatic niche through the CXCR4/CXCL12 axis [100,109] and can dock to the BM endothelial cells (ECs) through IGF-1R, subsequently migrating toward IGF-1 in the BM stroma [115]. BM, bone marrow; CCR1/CCL5, CC chemokine receptor 1/CC chemokine ligand 5; CXCR1, C-X-C motif chemokine receptor-1; ECM, extracellular matrix; EMT, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; IL-8, interleukin-8; MMP-9, matrix metalloproteinase-9; MSC, mesenchymal stromal cell; NB, neuroblastoma. Color images are available online.