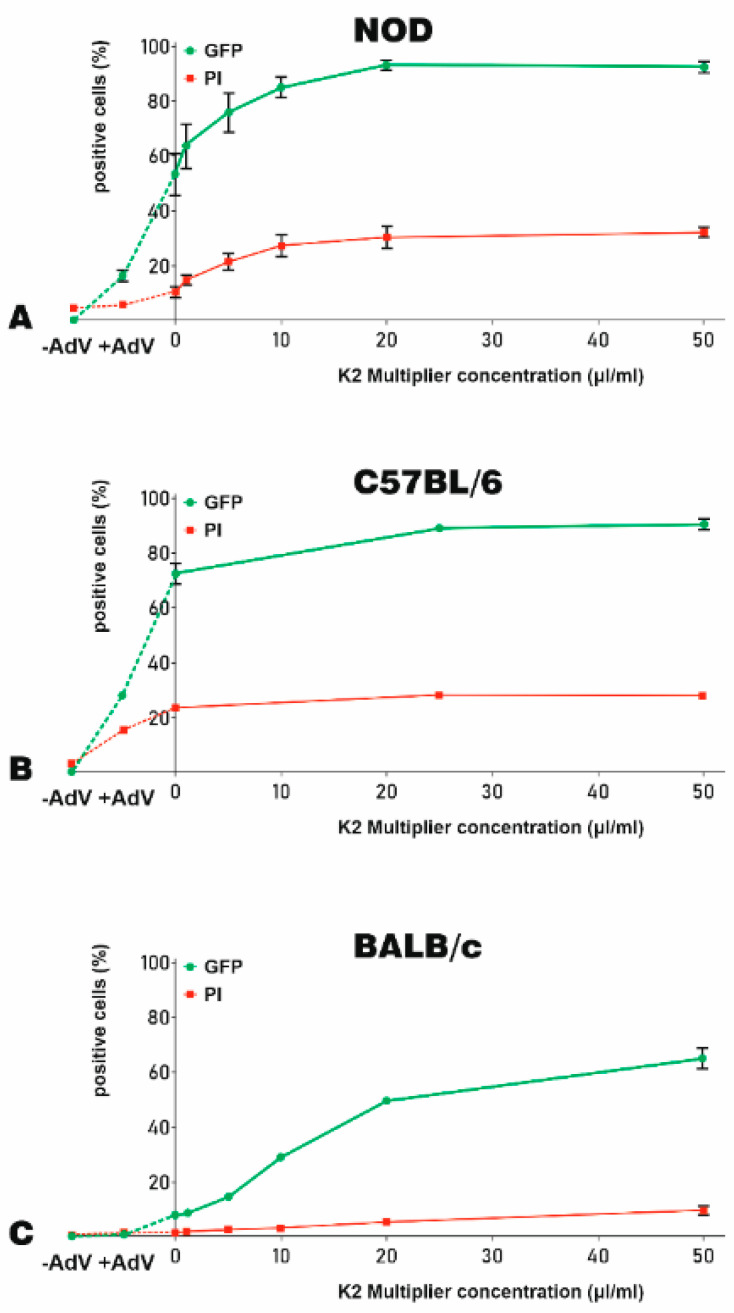
Figure 4.
The optimization of K2M for adenoviral transduction of murine MSC. The efficacy of K2M to increase the adenoviral transduction of MSC-derived from NOD (A), C57BL/6 (B), and BALB/c (C) mice were expressed as % of GFP-positive cells (green lines). The K2M induced cytotoxicity was indicated by the % of PI-positive, dead cells (red lines). To optimize the concentration of K2M needed for transduction, MSC were incubated with increasing K2M concentrations (up to 50 μL/mL) for 90 min. Then, the adenovirus–K2TR complexes (5 μL/mL K2TR and 250 TU/cell adenoviral particle) were added to the cells. The percentage of GFP-positive cells and PI-positive cells at 48 h after transduction was determined by flow cytometry. The same fractions were evidenced also for untransduced cells (−AdV) and NOD-, C57BL/6- and BALB/c-MSC transduced with the adenovirus alone (+AdV), which were linked by a dotted line in the left side of the graphs.