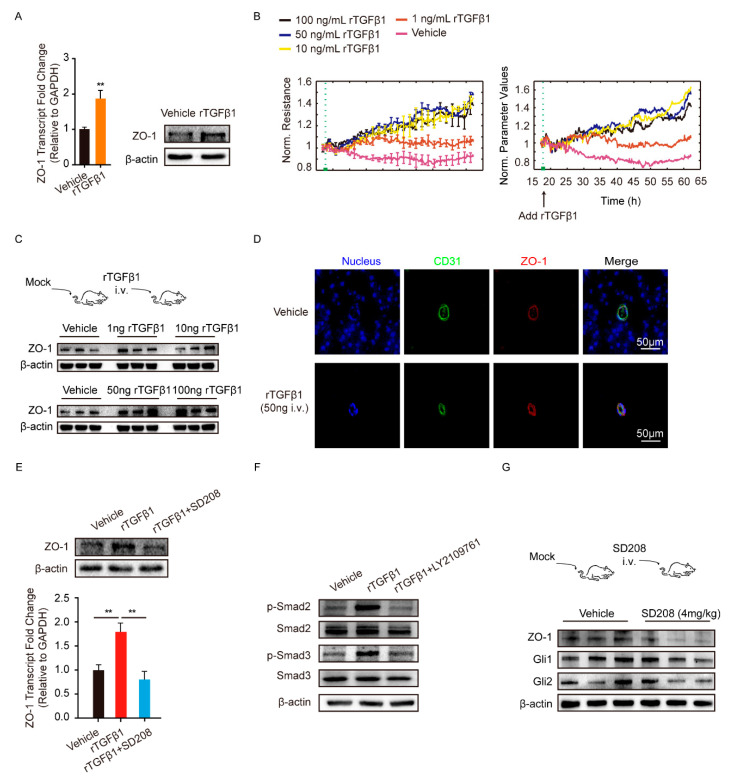
Figure 2.
TGFβ1 treatment enhanced BMECs tight junction protein ZO-1 expression. (A) The rTGFβ1 treatment (50 ng/mL) on the expression of ZO-1 in monolayer hBMECs. ** p < 0.01. (B) The effect of rTGFβ1 treatment on hBMECs barrier resistance monitored via ECIS system. The assay was performed with 5 replicates. (C) The effect of rTGFβ1 injection on the ZO-1 expression in mouse brains (n = 3). The β-actin was used as the loading control for the blotting. (D) IF demonstrated the ZO-1 expression on BMECs of the mice in response to rTGFβ1 treatment (50 ng, i.v.). BMECs were marked with CD31 in green. Scale bars indicated 50 μm. (E) The effects of rTGFβ1 treatment (50 ng/mL) and TGFβ1 signaling on the expression of ZO-1 in hBMECs. The qPCR assays were performed in triplicate, and data are represented as mean ± SEM. ** p < 0.01. (F) The phosphorylation activation of Smad2 and Smad3 in hBMECs by the treatment of rTGFβ1 (50 ng/mL). (G) The effects of SD208 injection (4 mg/kg i.v.) on the expression of ZO-1, Gli1 and Gli2 in mouse brains (n = 3). The β-actin was tested as the loading control. Results of 3 mice in each group were randomly presented.