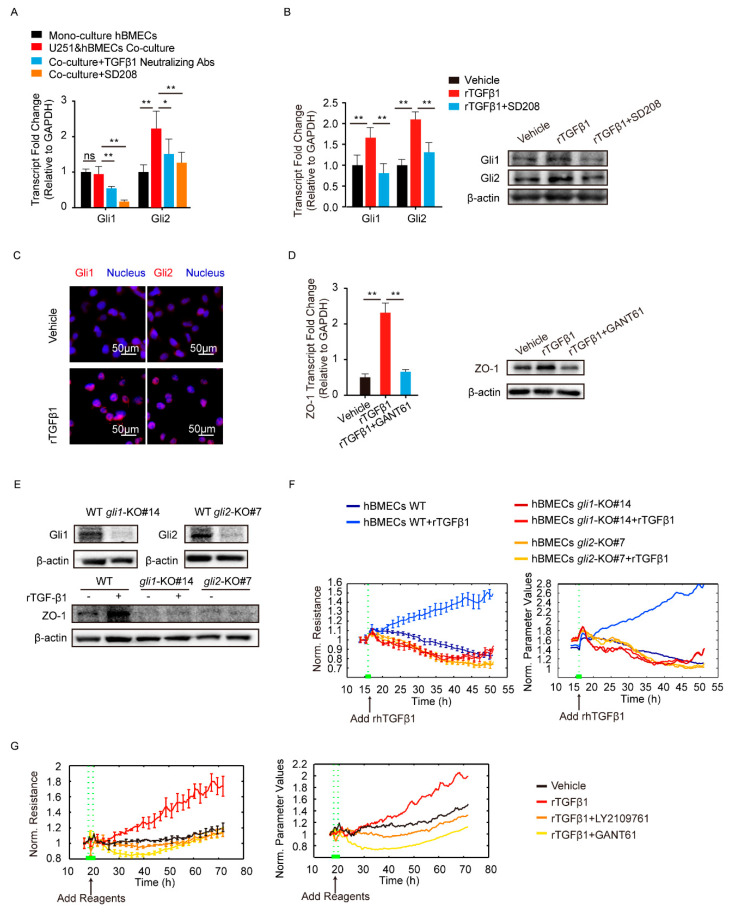
Figure 4.
TGFβ1 enhanced ZO-1 expression via non-canonical hedgehog signaling. (A) The transcription of Gli1 and Gli2 in mono-culture hBMECs and the co-culture of hBMECs with or without TGFβ1 neutralizing antibody (10 μg/mL) or SD208 (10 μM). * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01. (B) The expression of Gli1 and Gli2 in response to rTGFβ1 (50 ng/mL) with or without SD208 (10 μM) pretreatment via Western blot and qPCR. ** p < 0.01. (C) Nucleus translocation of Gli1 and Gli2 in hBMECs in response to TGFβ1 (50 ng/mL) via IF. Scale indicates 50 μm. (D) The expression of ZO-1 in hBMECs in response to TGFβ1 (50 ng/mL) with or without GANT61 (10 μM) via Western blot and qPCR. ** p < 0.01. (E) The gli1 and gli2 deletion in hBMECs through CRISPR/Cas9, and the expression of ZO-1 in both WT cells and KO cells in response to TGFβ1. (F) ECIS assays analyzing the barrier resistance of the WT cells and the gli1 or gli2 KO cells with the addition of TGFβ1 (50 ng/mL). (G) ECIS assays showing the effects of TGFβ1 (50 ng/mL), together with LY2109761 (10 μM) or GANT61 (10 μM), on the barrier function of monolayer hBMECs.