Figure 2.
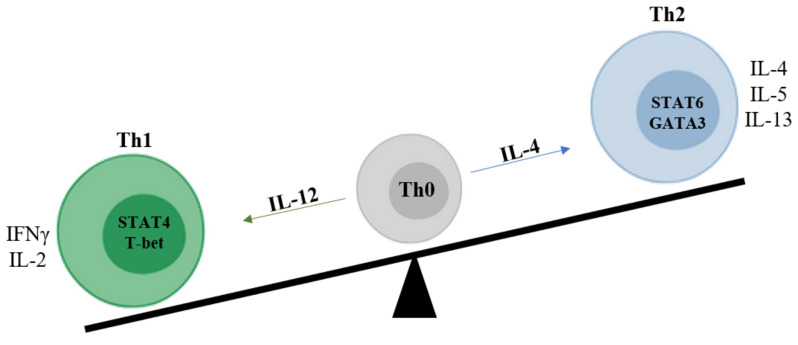
Th1-Th2 imbalance. Upon T-cell activation, IFN-γ, and IL-12 induce the expression of T-bet and STAT-4, which is involved in the differentiation of naïve CD4+ T cells into Th1 lymphocytes. Th1 cells predominantly produce pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IFN-γ and IL-2. In contrast, IL-4 induces the GATA-3 transcription factor and the consequent polarization of naïve T cells into Th2. Th2 cells produce anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13. Several studies have suggested that pSS is related to abnormal Th1 activation and SGs infiltration. It is supported by the presence of elevated levels of IFN-γ in serum and Th1 cells in blood. Furthermore, T cells expressing a high level of IFN-γ and STAT-4 mRNA have been found in SGs from pSS patients. This Th1/Th2 imbalance, generally observed in various chronic inflammatory disorders, is not easily understood because of a limited number of studies. Abbreviations: IFN-γ:interferon gamma; IL-: interleukin; pSS: primary Sjögren’s syndrome; STAT: signal transducer and activator of transcription; T-bet: T-Box Transcription Factor 21; Th1: type 1 helper cells; Th2: type 2 helper cells.