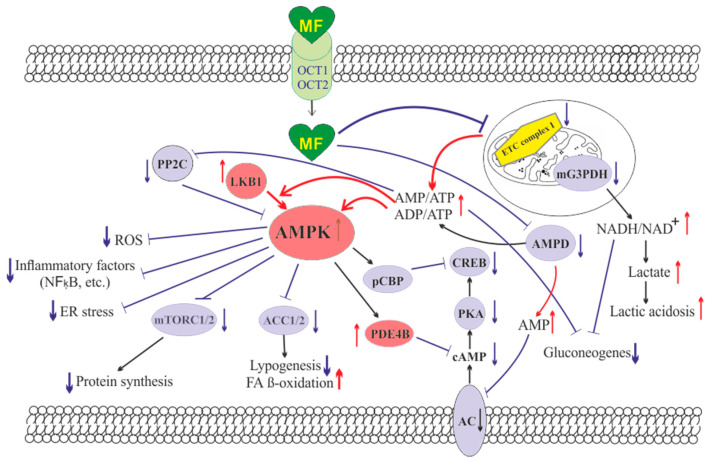
Figure 1.
The cellular mechanisms of metformin action which are carried out by activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase and inhibition of the mitochondrial electron transport chain complex I. Abbreviations: AC, adenylyl cyclase; ACC1/2, acetyl-CoA carboxylases 1 and 2; AMPD, AMP deaminase; AMPK, the heterotrimeric AMP-activated protein kinase consisting of the α1/2 (the target for activation phosphorylation at the Thr172), β1/2 and γ1/2/3 subunits; CREB, cAMP-activated transcription factor (cAMP response element-binding protein); ETC complex I, the mitochondrial NADH-dehydrogenase complex, the first complex of the respiratory electron transport chain; FA, fatty acids; LKB1, liver kinase B1; mG3PDH, mitochondrial glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; mTORC2, the mTOR complex 2; NFκB, nuclear factor κB; OCT1/2, the organic cations transporters 1 and 2; pCBP, the Ser436-phosphorylated form of CREB-binding protein with acetyltransferase activity, a co-activator of the factor CREB; PDE4B, cAMP-specific 3′,5′-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4B; PKA, cAMP-dependent protein kinase; PP2C, protein phosphatase 2C; ROS, reactive oxygen species.