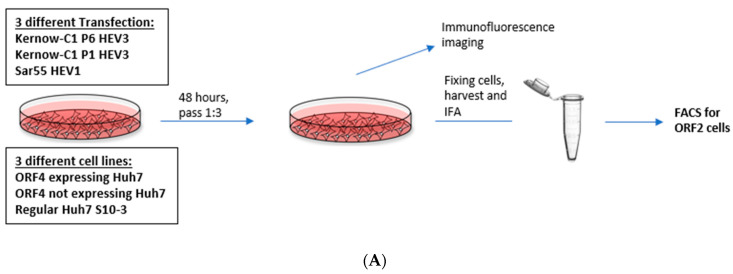
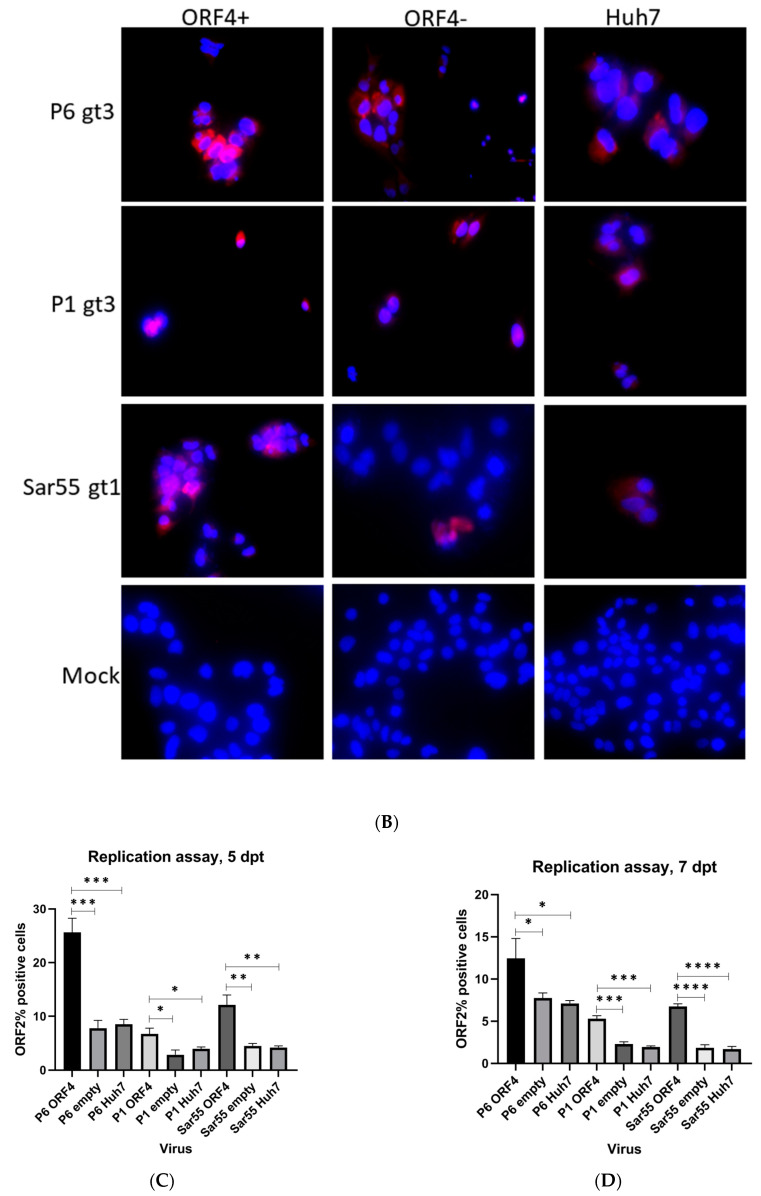
Figure 4.
Presence of ORF4 from gt1 enhances the gt3 HEV and gt1 HEV replication. (A) Workflow of HEV transfection of target cells. ORF4+, ORF4− and Huh7 cell lines were transfected with in vitro-transcribed capped HEV mRNA (P1, P6 and Sar55). Each cell line was grown in DMEM with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (HI-FBS). After 48 h, cells were passed 1:3. At 5 and 7 dpt, cells were harvested and used to detect HEV ORF2-positive cells. (B) Immunofluorescence detection of HEV ORF2 antigen in methanol-fixed ORF4+, ORF4−, Huh7 cell lines and respective mock cells after 5 dpt. Cells are stained with goat anti-rabbit IgG H&L combined with anti-rabbit Alexa fluor 594 (red), and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue). Images serve to validate antibody staining specificity and are not necessarily representative images as most fields are devoid of antigen staining. (C,D) Flow cytometry quantification of ORF4+, ORF4− and Huh7 cells transfected with the capped RNA transcripts of the HEV gt3 (P1 and P6) strains and HEV gt1 (Sar55) strain, performed at 5 and 7 dpt. Samples were fixed in methanol and probed with rabbit anti-ORF2 followed by goat anti-rabbit PE antibodies. Each bar (mean ± SEM) represents separate transfections stained in parallel and display the mean of three independent biological experiments with nine replicates per sample (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.001 t-test). Statistically significant difference exists between ORF4+ cell lines transfected with HEV gt3 (P6, P1) and gt1 (Sar55) strains verses other cell lines respectively transfected with similar strains.