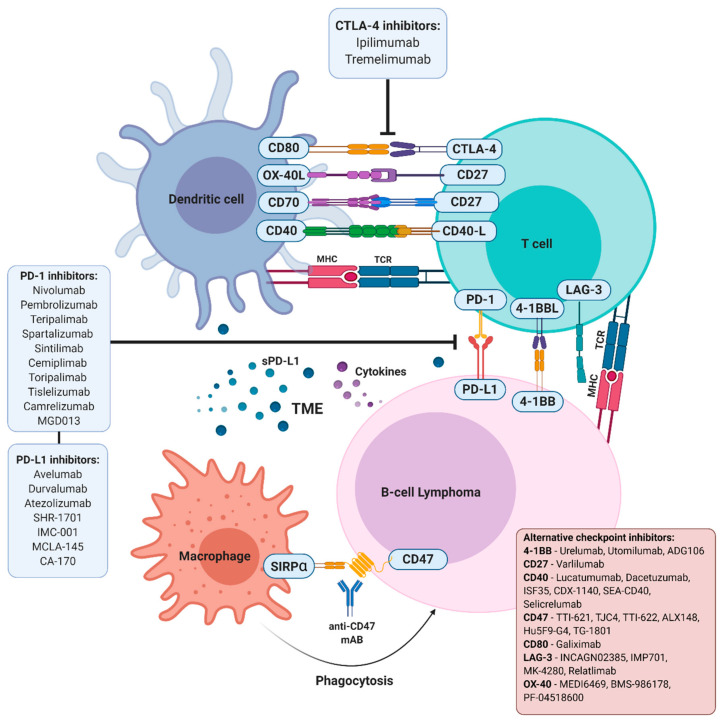
Figure 1.
Therapeutic approaches based on immune checkpoint blockade in B-cell lymphomas. Different therapeutic strategies to block PD-1/PD-L1 interaction are under clinical development in order to prevent PD-1-mediated attenuation of TCR signalling, allowing for activity restoration of exhausted CD8+ T-cells. CTLA-4 inhibition by monoclonal antibodies may induce tumour rejection through direct blockade of CTLA-4 competition for CD-80 (B7-1) and CD-86 (B7-2) ligands, which enhances CD28 costimulation and, thus, activation. Alternative immune checkpoint molecules expressed on tumour cells or immune cells in the TME can be simultaneously modulated to restore an effective antilymphoma immune response.