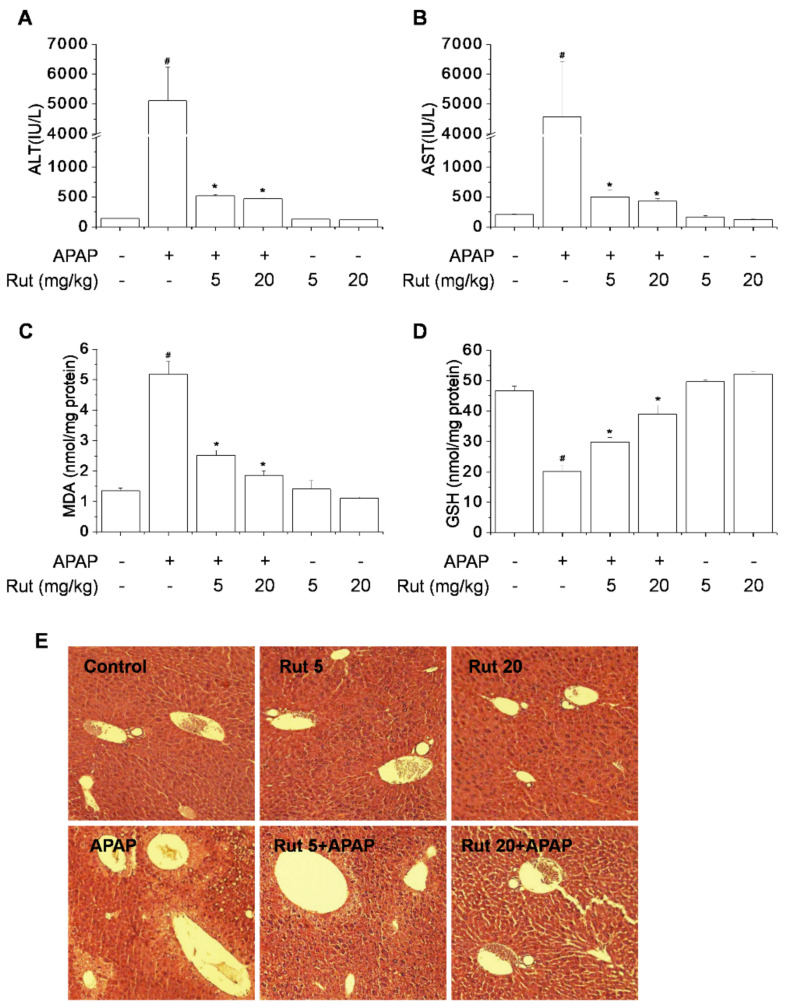
Figure 1.
Protective effect of Rut in acetaminophen (APAP)-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Mice were orally administered 5 or 20 mg/kg of Rut once daily for 7 consecutive days. Control and APAP-treated groups received only the appropriate vehicle orally. After fasting for 12 h, mice were intraperitoneally injected with 300 mg/kg APAP and euthanized after 8 h. Hepatotoxicity was analyzed by measuring serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) (A) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) (B) activities and hepatic malondialdehyde (MDA) (C) and glutathione (GSH) (D) contents. Representative hematoxylin and eosin-stained liver samples for histopathological analysis at 100× magnification (E). # Significantly different from the control (p < 0.05). * Significantly different from the APAP-treated group (p < 0.05).