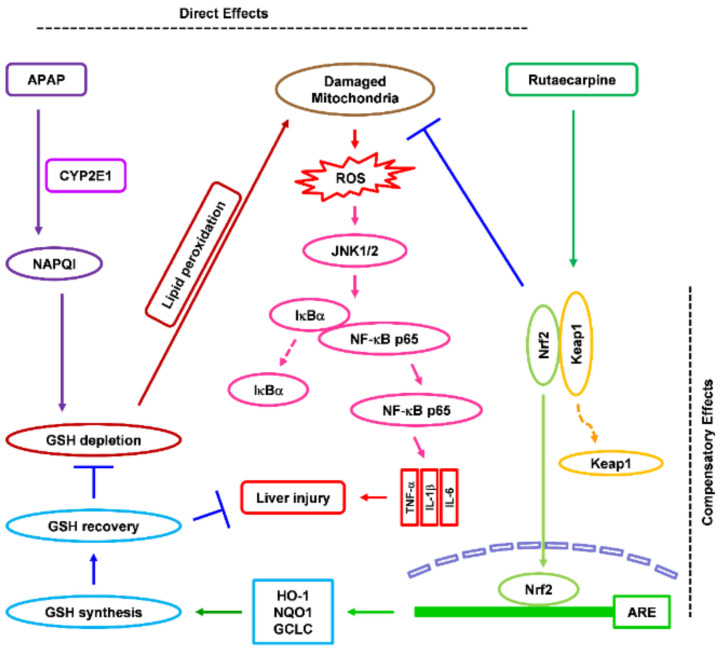
Figure 7.
Protective effect of Rut in APAP-induced liver damage in mice. Direct effect. APAP is converted by CYP2E1 to NAPQI, a toxic metabolite. NAPQ1 depletes intracellular GSH and damages mitochondria by binding to mitochondrial proteins. Rut pretreatment inhibits the expression of CYP2E1, ameliorating intracellular GSH depletion, and inhibits lipid peroxidation, thereby preventing APAP-mediated mitochondrial damage. Compensatory effect. Rut pretreatment increases the nuclear translocation of Nrf2 by alleviating its inhibition by Keap1, causing sustained activation of Nrf2 in the mouse liver. Prolonged activation of Nrf2 increases the GSH content in the mouse liver, eliminating NAPQI and protecting the liver against APAP-induced oxidative stress.