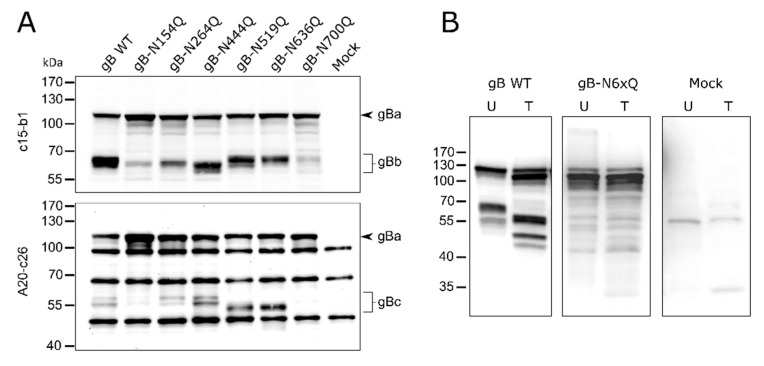
Figure 2.
Expression and glycosylation analysis of PrV gB N-glycosylation mutants. (A) Lysates of RK13 cells transfected with expression plasmids for the indicated gB variants were separated by SDS–PAGE under reducing conditions. Lysates of cells transfected with empty vector pcDNA-3 served as a negative control (Mock). Blots were either probed with the monoclonal antibody (mAb) c15-b1, directed against the N-terminal subunit (gBb) of furin-cleaved gB (upper panel), or with mAb A20-c26 (lower panel) recognizing the C-terminal gB subunit (gBc). Signals of uncleaved gB (gBa) or furin-cleaved gB subunits (gBb and gBc) are labeled by arrowheads and braces. The molecular masses of marker proteins are indicated. Representative blots from three independent experiments are shown. (B) Analysis of N-linked carbohydrates in gB. Lysates of RK13 cells expressing PrV wild-type (WT) gB or gB-N6xQ were either left untreated (U) or treated (T) with PNGase F. Samples were separated by SDS–PAGE under reducing conditions, and blots were probed with a monospecific rabbit antiserum against PrV. Three independent experiments were performed, and one representative blot is shown.