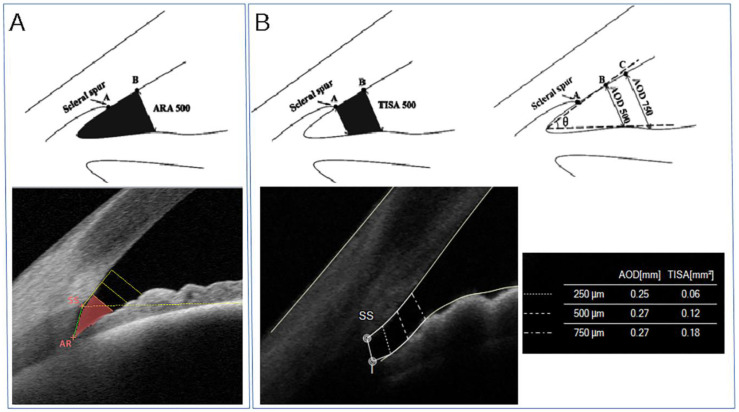
Figure 3.
(A) Top panel. Schematic diagram of the angle-recess area at 500 microns from the scleral spur (ARA500, black area). Bottom panel. Tomey Casia 2 AS-OCT scan (Nagoya, Japan) of the angle showing in vivo ARA500 (red area). ARA is defined as the triangular area bordered by the anterior iris surface, corneal endothelium, and a line perpendicular to the endothelium drawn from a point anterior to the scleral spur to the iris surface. (B) Top panel. Schematic diagram of the trabecular iris-space area at 500 microns from the scleral spur (TISA500, black area, top left panel) and the angle-opening distance at 500 and 750 microns from the scleral spur (AOD500 and AOD750, respectively, top right panel). Bottom panel. MS-39 AS-OCT scan (CSO, Florence, Italy) of the iridocorneal angle showing in vivo TISA and AOD. AOD is the perpendicular distance from the iris to the trabecular meshwork, which can be measured at different distances anterior to the scleral spur, such as 250, 500, 750 microns (AOD250, AOD500, AOD750, respectively). TISA, which again can be evaluated at several distances from the scleral spur (SS), is defined as the trapezoidal area with the following boundaries: anteriorly, the AOD; posteriorly, a line perpendicular to the plane of the inner corneoscleral wall drawn from the scleral spur to the opposing iris; superiorly, the inner corneoscleral wall; and inferiorly, the anterior iris surface.