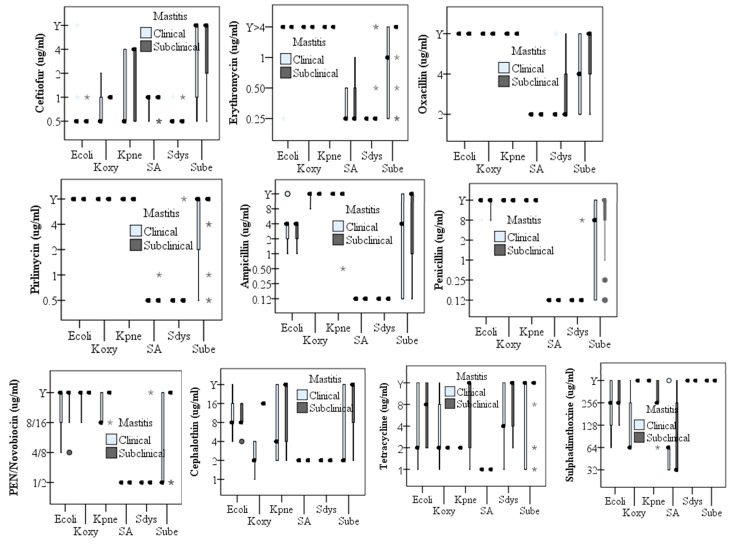
Figure 2.
Box plot of minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values (µg/mL) of six bacterial species isolated from clinical and subclinical bovine mastitis against commonly used antimicrobials in dairy farms. In the box plot, the median MIC values are shown by dark dots and the standard error is shown by a vertical bar. The star symbol and white dots showed isolates with outlier MIC values. Ecoli: E. coli, Koxy: K. oxytoca, Kpne: K. pneumoniae, SA: Staph. aureus, Sdys: Strep. dysgalactiae, Sube: Strep. uberis. The “Y” value on the Y-axis was for isolate with MIC value above the maximum antimicrobial concentration coated on the Sensititre plate. The dark dots indicated the median MIC value, which corresponds to half (50%) of the isolates for respective bacterial species isolated from clinical or subclinical mastitis. For penicillin, penicillin-novobiocin, erythromycin, oxacillin, and pirlimycin all Gram-negative isolates had MIC value above the concentration of the antimicrobials coated on the Sensititre plate (Y > 4 µg/mL) because of their intrinsic resistance to these antimicrobials.