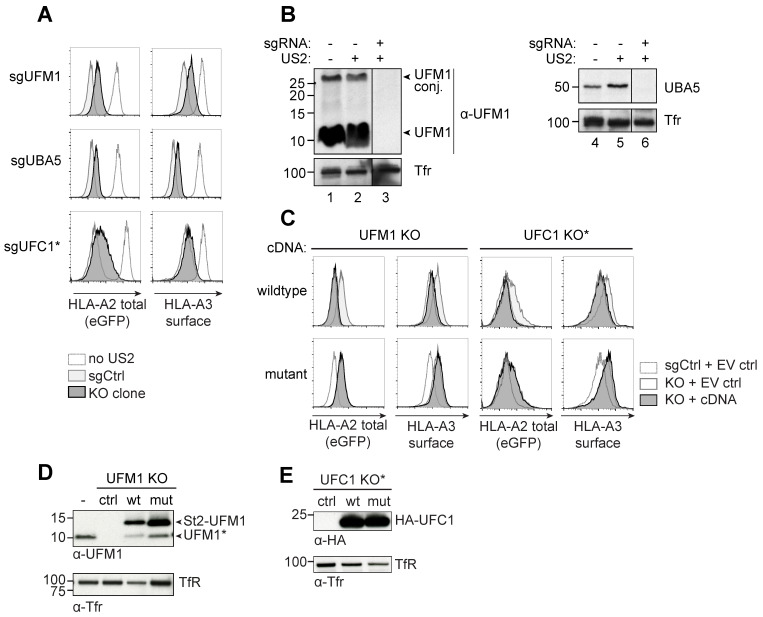
Figure 3.
Clonal knockout cell lines for UFM1 and UBA5 show stable HLA-I rescue in the presence of HCMV US2. (A) U937 cells expressing HLA-A2-eGFP and US2 were transduced with sgRNAs targeting UFM1, UBA5, or UFC1. At 12 d.p.i., single HLA-A2-eGFP+ cells from the sgUFM1 and sgUBA5 cell lines were cloned by FACS and allowed to expand for ~8 weeks. Expression of HLA-A2-eGFP and endogenous HLA-A3 was assessed by flow cytometry. One representative clone is shown. A polyclonal cell population of UFC1-targeted U937 cells (indicated with *) expressing eGFP-tagged HLA-A2 and US2 was also stained for HLA-A3 at 10 d.p.i. These cells show a modest rescue of HLA-A2 and HLA-A3, similar to the clonal lines for UFM1 and UBA5. (B) Western blot analysis of the clonal cell lines established for UFM1 and UBA5. Cell lysates from the cell lines shown in A were prepared in 1% Triton X-100 and stained for the gene that was targeted by the CRISPR sgRNAs. Tfr was used as a loading control. (C) sgRNA-resistant wildtype, or mutant cDNAs encoding inactive UFM1 or UFC1 were transduced into the knockout clone or polyclonal cell line (for UFC1) shown in A and B. Whereas a wildtype cDNA for UFM1 reverts the HLA-A2-eGFP- and HLA-A3 rescue phenotype observed in knockout clones, the inactive mutant cDNA does not. For mutant UFM1, the four C-terminal amino acids, including glycine used for substrate conjugation, were deleted (ΔVGSC). For the inactive UFC1 cDNA, the active site cysteine essential for catalytic activity was mutated into serine (C116S). UBA5 cDNAs did not express well, therefore this cDNA was excluded from the experiment. (D) Immunoblots showing UFM1 protein expression in the knockout clones following the introduction of the cDNAs expressed in C. The UFM1 construct is detected using a UFM1-specific antibody. Upon expression of StrepII-tagged UFM1, a product migrating at the molecular weight of untagged UFM1 (UFM1*) is consistently observed, suggesting this product may be a truncated variant of the ST2-UFM1 construct. (E) Immunoblotting of the UFC1 cDNAs used in C. The HA-tagged UFC1 construct is detected using an anti-HA antibody.