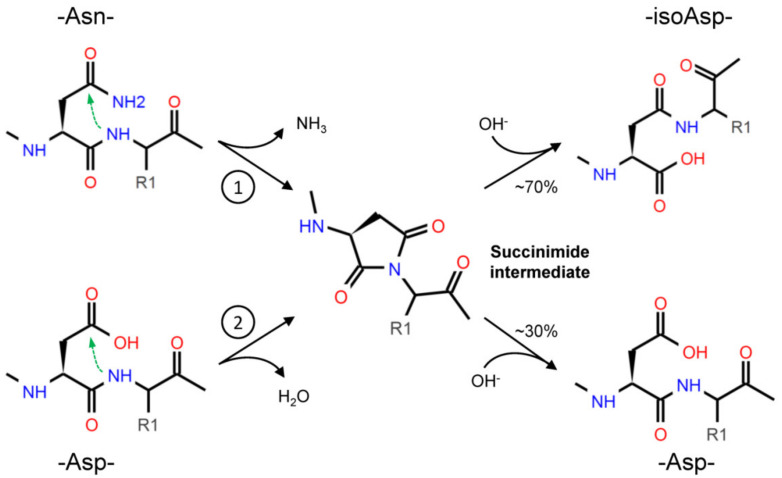
Figure 1.
Asparagine (Asn) deamidation (1) starts with the nucleophilic attack (green arrow) of the α-amino group, in the peptide bond, to the amide group in the side chain. The cyclic succinimide intermediate is then rapidly hydrolyzed to a mixture of Aspartate (Asp) and isoAspartate (isoAsp), with the prevalent production of the latest (about 70% vs. 30%) due to the asymmetry of the succinimide [17]. The formation of isoAsp can also occur from Asp dehydration (2), with a similar nucleophilic attack, but this reaction occurs at a slower rate.