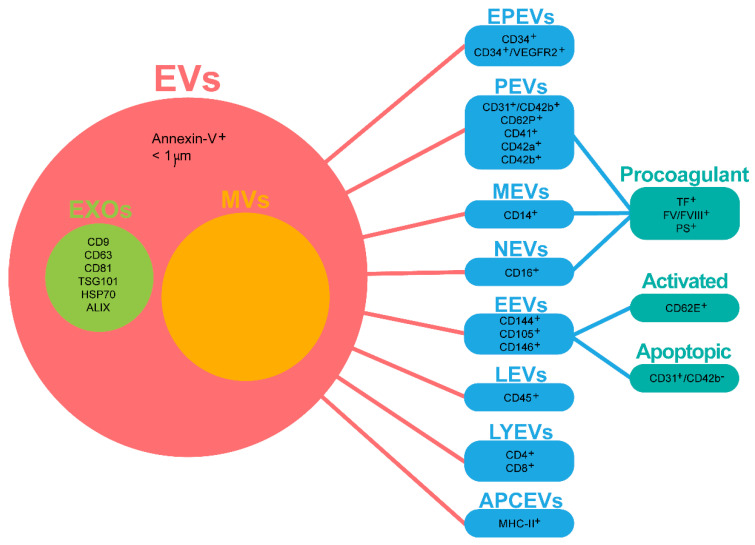
Figure 1.
Nomenclature and cell-specific subtypes of circulating extracellular vesicles. In this review, focus will be given to extracellular vesicles (EVs), which include both exosomes (EXOs) and microvesicles (MVs). EXOs were distinguished when appropriate markers were identified. This decision was supported by the known overlap in size/marker definitions between EXOs and MVs (also called ectosomes or microparticles) and by the fact that most studies here included referred to MVs as broad EVs with size < 1 μm and/or annexin-V+. Additionally, cell-specific subtypes of the most common circulating EVs were categorized and uniformed according to the studies here reviewed. For a full list of other markers, please see [51,52,62]. APCEVs, antigen-presenting cell-derived vesicles, EEVs, endothelial-derived vesicles, EPEVs, endothelial progenitor cell-derived vesicles, EVs, extracellular vesicles, EXOs, exosomes, FV/FVII, coagulation factors V/VII, LEVs, leucocyte-derived vesicles, LYEVs, lymphocyte-derived vesicles, MEVs, monocyte-derived microvesicles, NEVs, neutrophil-derived microvesicles, PEVs, platelet-derived vesicles, PS, phosphatidylserine and TF, tissue factor.