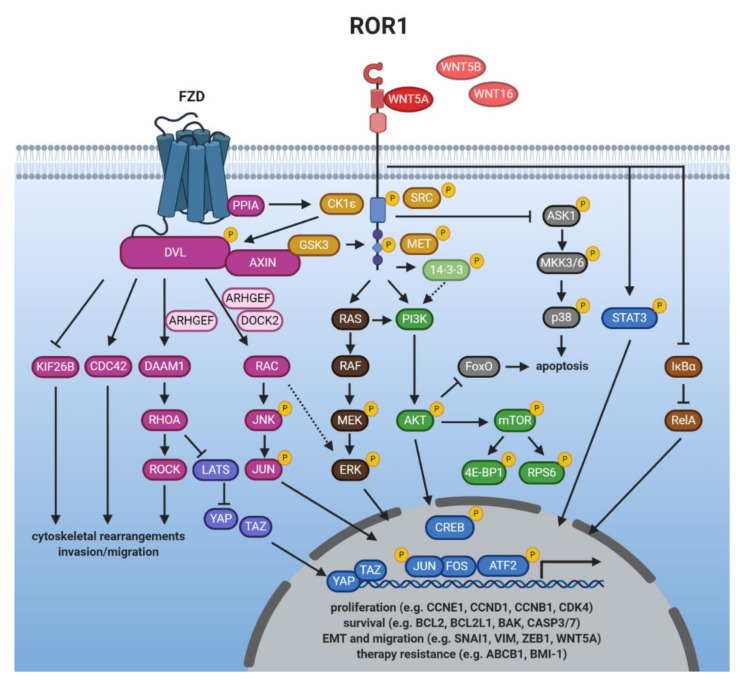
Figure 2.
ROR1 signaling. WNT/ROR1 signaling is induced by binding of a non-canonical WNT ligand, which triggers the formation of a complex between ROR1 and ROR2, or ROR1 and a FZD receptor, respectively. Signal transduction is mediated by the phosphorylation of ROR1 by several kinases (orange) which on the one hand results in the inhibition of anti-apoptotic pathways (grey), while on the other hand activates downstream pathways such as WNT/PCP (magenta), MAPK/ERK (dark brown), PI3K/AKT (green) or NF-κB (light brown). These either trigger cytoskeletal rearrangements associated with enhanced tumor cell migration, or induce a transcriptional response (blue) leading to the expression of genes which promote cell proliferation, survival, EMT, or therapy resistance.