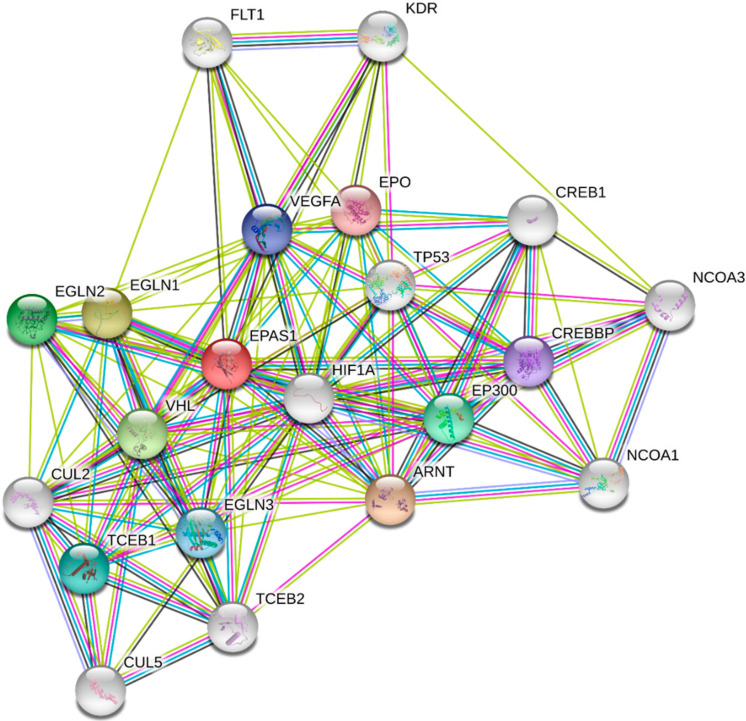
Figure 3.
The protein–protein interaction network of HIF-1α obtained from String v11 database [29]. The colored lines of the edges represent the existence of different types of evidence used in predicting the associations (green: neighborhood evidence; blue: co-occurrence; purple: experimental evidence; light blue: database evidence; black: co-expression evidence). The HIF-1α interacting proteins are (in alphabetical order): ARNT: aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator; CREB1: cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein 1; CREBBP: CREB-binding protein; CUL2: cullin2; CUL5: vasopressin-activated calcium-mobilizing receptor 1; EPAS: endothelial PAS domain protein 1, HIF-2α; EGLN1: Egl nine homolog 1; EGLN2: Egl nine homolog 2; EGLN3: Egl nine homolog 3; EPO: erythropoietin; EP300: histone acetyltransferase p300; FLT1: vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1; KDR: vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2; NCOA1: nuclear receptor coactivator 1; NCOA3: nuclear receptor coactivator 3; TCEB1: elongin-C; TCEB2: elongin-B; TP53: cellular tumor antigen p53; VEGFA: vascular endothelial growth factor; VHL: Von Hippel–Lindau disease tumor suppressor.