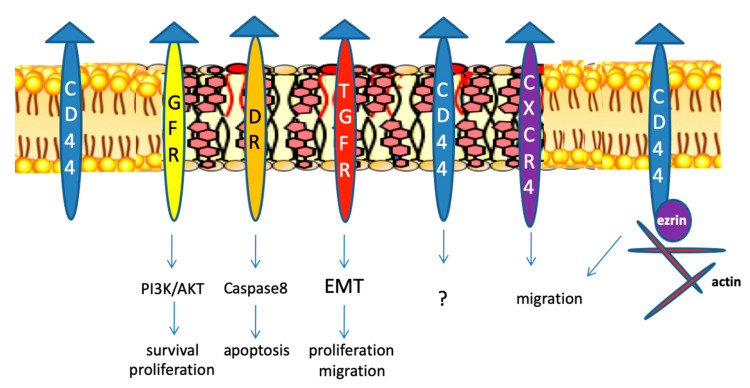
Figure 1.
Roles of lipid rafts in cancer NO. Lipid rafts are involved in proliferation, apoptosis, migration, cell adhesion, and metastasis. Many proteins involved in cancer are localized in rafts. For example, growth factors receptors (GFR) through activation of PI3K/AKT or MAPK pathways lead to survival and proliferation; dead receptors (DR) such as TRAIL and Fas activate caspase 8 and the apoptotic cascade; the chemokine receptor CXCR4 activation leads to migration; the transforming growth factor-1 β receptor (TGFR) is involved in epithelial to mesenchimal transition (EMT). CD44 is localized in rafts, but its role is unclear (2). When it moves out of them, it is able to interact with the metalloproteinase 10 [90] and with ezrin, leading to actin remodelling and cell migration. Triangles: ligands of the receptors. See explanations and references in the text.