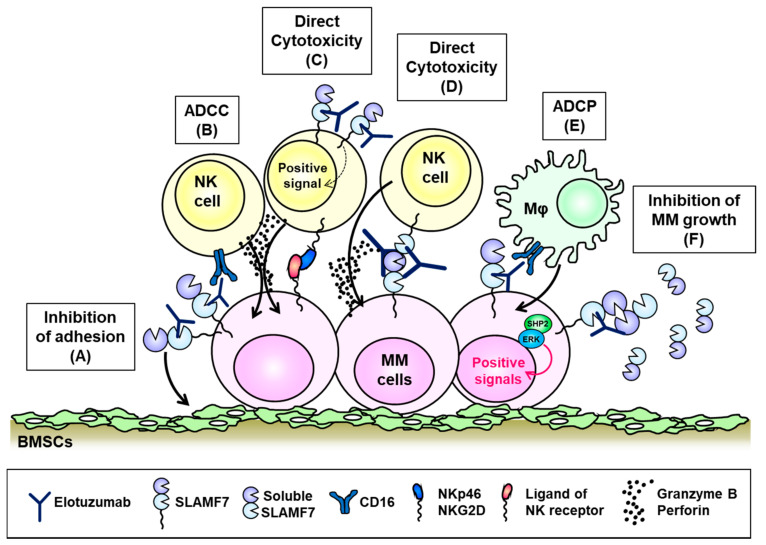
Figure 4.
The biological function of the signaling lymphocytic activation molecule family receptor (SLAMF) 7 on multiple myeloma (MM) cells and mechanism of action of elotuzumab. (A) On MM cells, SLAMF7 is associated with adhesion to bone marrow stroma cells (BMSCs) and elotuzumab blocks MM cell adhesion to BMSCs. Elotuzumab stimulates robust natural killer (NK) cell-mediated antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) via the Fc–CD16 interaction (B), directly induces activating signal transduction in NK cells (C), improves NK-cell-mediated cytotoxicity in response to the SLAMF7–SLAMF7 interaction (D), and enhances macrophage (Mφ)-mediated antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis through the CD16 receptor (E). (F) SLAMF7 promotes MM cell growth via SHP2–ERK signaling in response to binding with soluble SLAMF7 (sSLAMF7), and elotuzumab suppressed MM cell growth promoted by SLAMF7–sSLAMF7 interactions in vitro.