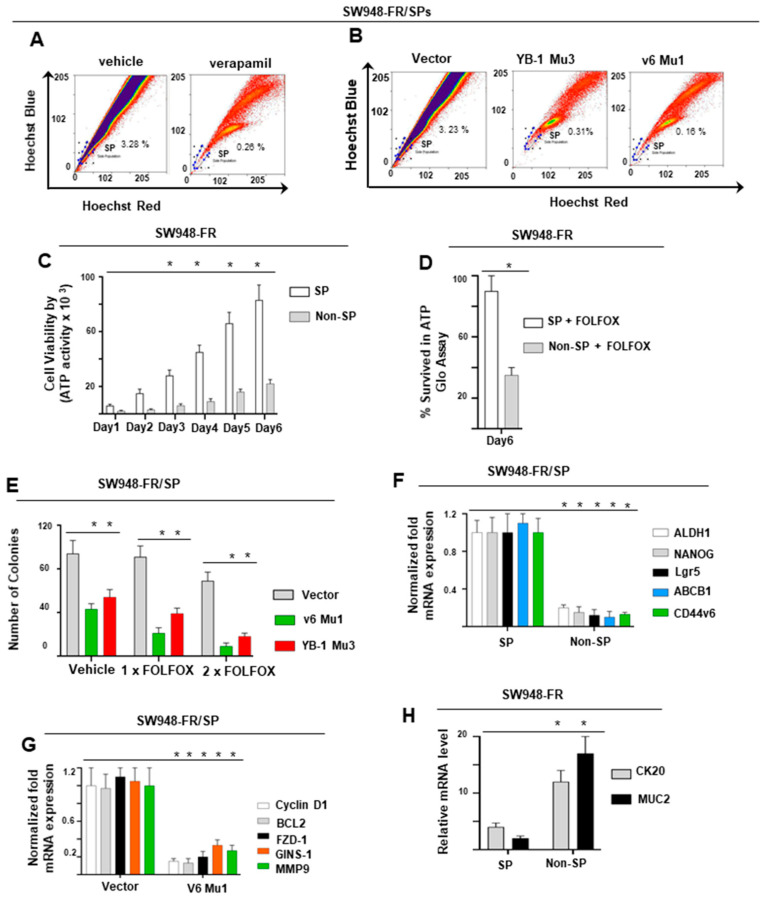
Figure 5.
CD44v6-YB-1 defines CIC-like SP cells. (A) SW948-FR cells labeled with Hoechst 33342 showed 3.3% of SP cells in the SP gated region. Following treatment with verapamil, the SP cells were reduced to 0.26%. (B) v6 Mu1 and YB-1 Mu3 regulate the side population. The SP cells were <10% of vector cells in the v6 Mu1 cells, and the YB-1-Mu3 SW948-FR cells. (C) Cell proliferation rates were measured by ATP GLO assay for SP and non-SP cells. SP cells underwent rapid proliferation compared with non-SP cells. (D) SP cells exhibited high resistance to 1 × FOLFOX whereas the non-SP cells were sensitive to 1 × FOLFOX. (E) CD44v6 and YB-1 knockdown in SW948-FR cells decreased the drug resistance. Control, v6 Mu1, and YB-1 Mu3 SW948-FR cells were treated with various doses of FOLFOX for 10 days in 3% FBS DMEM. Cell viability was assessed using the clonogenic assay. The clonogenicity of CD44v6-Mu1 cells was significantly decreased compared with YB-1-Mu3 cells. (F) Expressions of core stemness genes in SW948-FR/SP and non-SP cells by QPCR are shown. (G) Expressions of anti-apoptosis/stemness-related genes in vector and v6 Mu1 transfected SW948-FR/SP cells are shown. (H) Expressions of CRC differentiation genes in SW948-FR/SP and non-SP cells are shown. Each bar represents the means of three determinations ± SD. * p < 0.05 among the indicated groups compared to respective control group. FACs data are representative of three experiments.