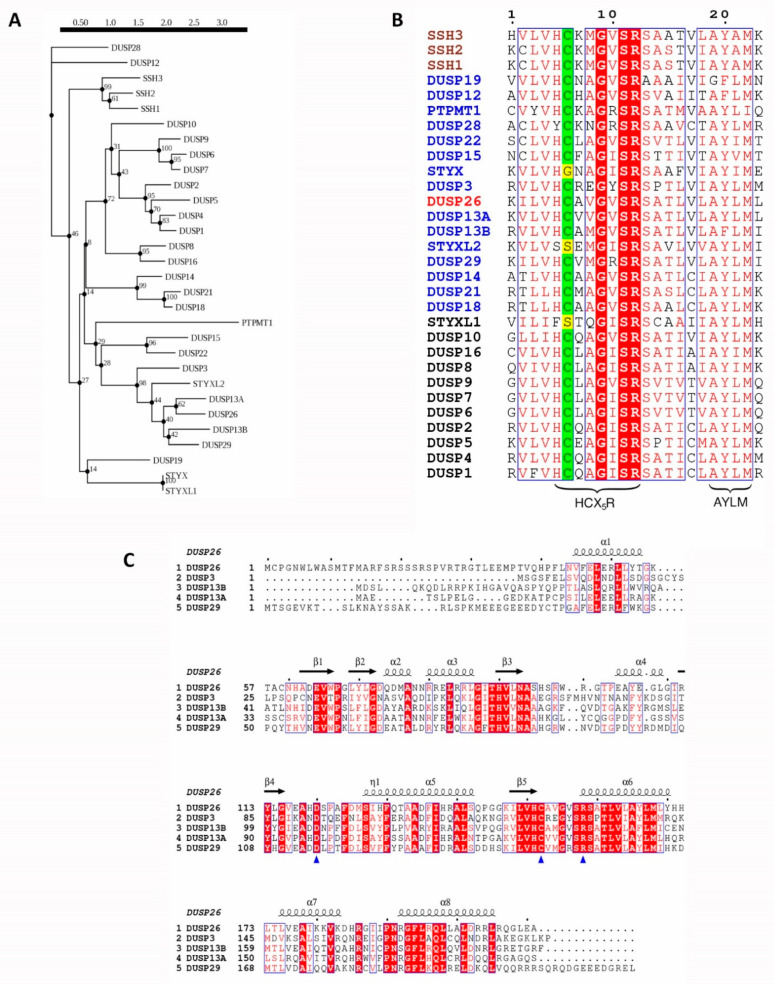
Figure 1.
Evolutionary analysis of human DUSP26 and its homologous proteins. (A) Phylogenetic tree of human DUSP26 and its 29 closest homologous proteins. Sequences were identified using the blastp program in the UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot database. Following this, sequences were mapped onto a phylogenetic tree using the Smart Model Selection in PhyML with 100 bootstrap replications applied [37,38]. (B) Protein sequence alignment of the active site region of DUSP26 and 29 closest homologous protein sequences. Catalytic cysteine highlighted in green; pseudo-catalytic residue of pseudophosphatases in yellow; MKP, aDUSP and SSH names are in black, blue and brown, respectively, and the DUSP26 name is in red. (C) Protein sequence alignment of DUSP26 and its closest homologues, excluding the pseudo-phosphatase STYXL2. Blue triangles pinpoint the catalytic triad and depicted above are the α-helices and β-sheet positions and of the DUSP26 structure. For sequence alignments, identical residues are displayed in white inside red boxes; residues with 70% similarity based on physico-chemical properties are displayed in red inside blue boxes; alignment generated using the ESPript 3.0 tool [39].