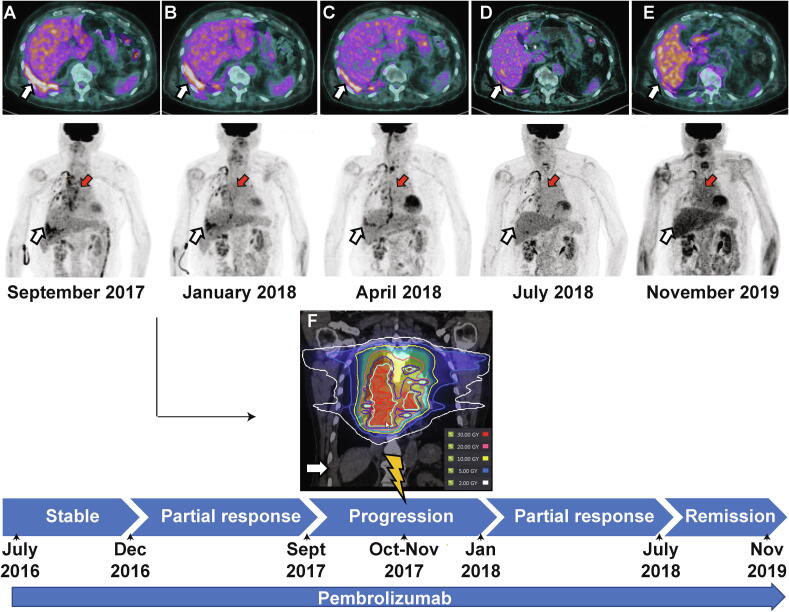
Fig 1.
Diagnostic and radiotherapy simulation imaging throughout the disease course. Axial and coronal (maximum intensity projection – MIP) 18FDG PET/CT scans corresponding to the timeline for treatment and disease status (from panel A to E). Red arrows indicate the mediastinal lesions that have been irradiated. White arrows indicate unirradiated right pleural lesions. Panel A (top) reflects the pre-RT status of a progressive disease on pembrolizumab (SUVmax 7.3). Panel B shows images 3 months after RT when the response to the irradiated and unirradiated lesions has begun (SUVmax 6.5) Panel C shows images 6 months after RT with complete response of the targeted mediastinal mass and partial response of the abscopal right pleural lesion (SUVmax 4). Panel D-E shows images 9 months and 24 months after the first RT with the patient in complete remission (SUVmax 2.8). Panel F shows the CT simulation image for radiotherapy planning, and the target volume in the mediastinum. Isodose lines represent total dose of 30 Gy (red), 20 Gy (orange), 10 Gy (yellow). The 2 Gy isodose line in white is far from the right abscopal pleural lesion. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)