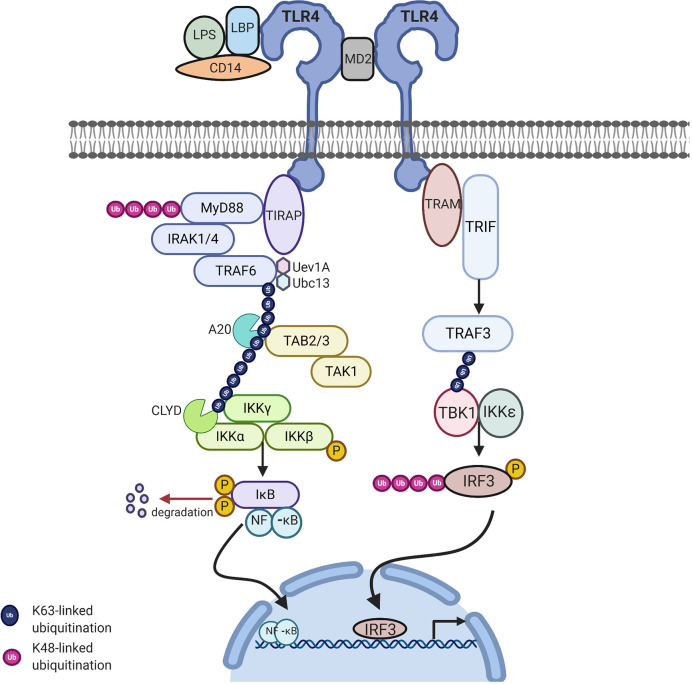
Figure 2.
TLR4 signaling via MyD88-dependent and independent pathway to activate NFkB related target genes: Upon stimulation of myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88 (MyD88) dependent pathway involves the activation of MyD88 which recruits IL-1 receptor-associated kinase-4 (IRAK-4). IRAK-4 phosphorylates IRAK-1 and allows tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6 (TRAF6) to associate with IRAK1. IRAK1/TRAF6 then activates TAK1, TAB1, and TAB2. The TRAF6, TAK1, TAB1, and TAB2 forms a larger complex with ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E32 variant 1 isoform A (Ubc13) and Uev1A which activates TAK1. Polyubiquitin chain is then removed by A20 and conserved cylindromatosis (CYLD). Activated TAK1 phosphorylates the IKK complex (IKKα. IKKβ and IKKγ) ultimately resulting in the translocation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) into the nucleus, resulting in the transcription of proinflammatory cytokines. MyD88 independent pathway involves TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β (TRIF) leading to the activation of TNF receptor associated factor 3 (TRAF3) and the translocation of interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) to the nucleus leading to IFNB gene transcription. Image made using BioRender.