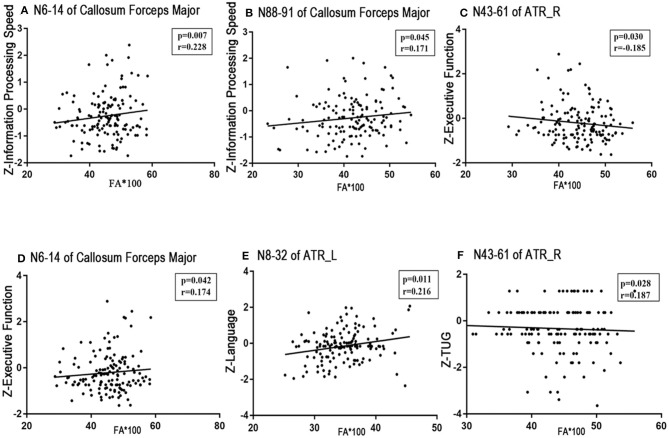
Figure 4.
Correlations between FA profiles and neuropsychological examinations. Partial correlation was conducted controlling for age, gender, years of education, history of hypertension, and history of LI/TIA in patients with CSVD. (A,B) Information processing speed was positively correlated with the mean FA values of the occipital lobe portion of the callosum forceps major (nodes 6–14, r = 0.228, p = 0.007; nodes 88–91, r = 0.171, p = 0.045). (C,D) Executive function was negatively related to the FA value of the intermediate component of the right ATR (nodes 43–61, r = −0.185, p = 0.030), whereas was positively correlated with the FA of the occipital lobe portion of the callosum forceps major (nodes 6–14, r = 0.174, p = 0.042). (E) Language function was positively correlated with the FA of anterior component of the left ATR (nodes 8–32, r = 0.216, p = 0.011). (F) TUG showed positive correlated with the FA value of the intermediate component of the right ATR (nodes 43–61, r = 0.187, p = 0.028). CSVD, cerebral small vessel disease; LI, lacunar infarction; TIA, transient ischemic attack; WMH, white matter hyperintensities; ATR, anterior thalamic radiation.