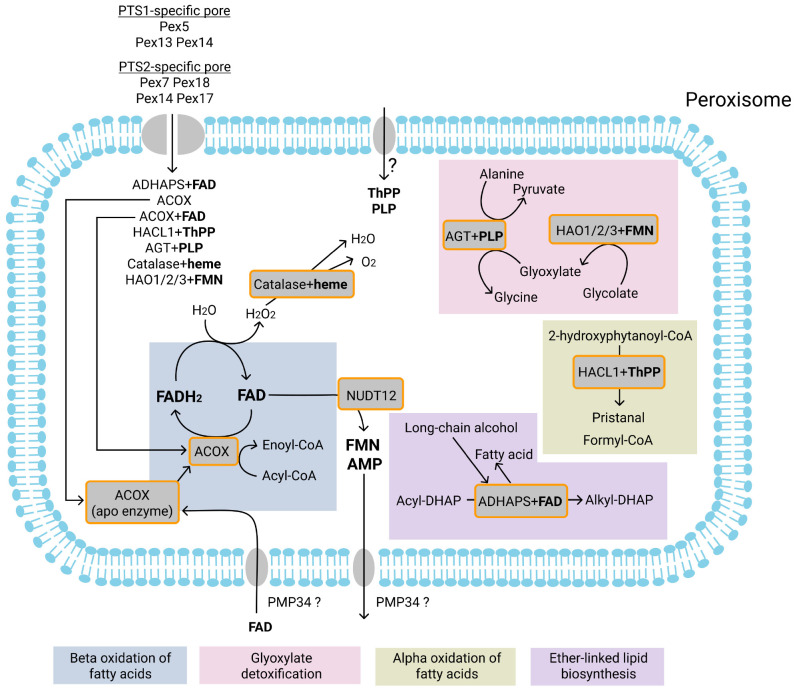
FIGURE 3.
Currently known FAD, PLP, ThPP, FMN, and heme-dependent enzymatic reactions in the peroxisomes and transport of FAD, PLP, ThPP, heme, FMN and AMP. Most of the peroxisomal matrix proteins are imported into peroxisomes via a PTS1-specific pore. Proteins may be imported as monomers or in a fully folded form complexed with their cofactor. Cofactors that may be co-imported with proteins are FAD (with ACOX and ADHAPS proteins), FMN (HAO1, HAO2, HAO3), ThPP (with HACL1), PLP (with AGT), and heme (with catalase). It has also been suggested that the PMP34 transporter can import free FAD into peroxisomes. In the peroxisome, FAD forms an active enzyme with apoenzyme ACOX. The pyrophosphatase NUDT12 may mediate the degradation of FAD to FMN and AMP. FMN and AMP are subsequently exported from peroxisomes, probably by PMP34. Acyl-CoA oxidases (ACOX) mediate the first (dehydrogenation) reaction of the beta-oxidation. During dehydrogenation, FAD is reduced to FADH2. FADH2 is re-oxidized by direct transfer of electrons to O2, resulting in the production of H2O2. H2O2 is degraded by the heme-dependent enzyme catalase to H2O and O2. It is unclear whether free ThPP or PLP are imported into peroxisomes. Alkyl-dihydroxyacetonephosphate synthase (ADHAPS) catalyzes the exchange in acyl-dihydroxyacetonephosphate (acyl-DHAP) of the acyl chain with long-chain alcohol through a non-redox mechanism. The ThPP-dependent enzyme 2-hydroxyacyl-CoA lyase (HACL1) catalyzes the cleavage of 2-hydroxyphytanoyl-CoA into pristanal and formyl-CoA during peroxisomal alpha-oxidation of phytanoyl-CoA. The PLP-dependent enzyme alanine-glyoxylate aminotransferase (AGT) catalyzes the transamination of glyoxylate to glycine during glyoxylate detoxification. The FMN-dependent enzymes 2-hydroxyacid oxidases (HAO1, HAO2, HAO3) catalyze oxidation of glycolate to glyoxylate. Enzymatic reactions or molecules belonging to the same metabolic pathway are marked with background color and listed at the bottom.