Fig. 5.
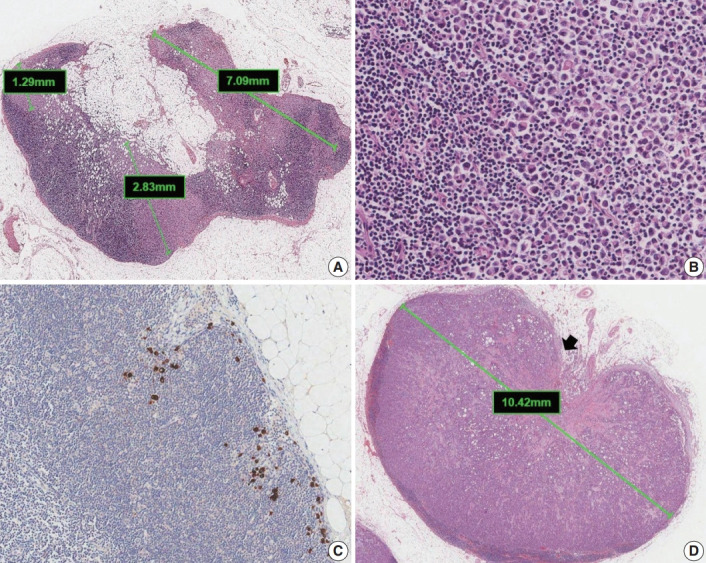
Classification of lymph node metastases. (A) Multiple clusters of tumor cells. N category is based on the size of the largest contiguous cluster of tumor cells. (B) Dispersed pattern of metastasis. Some lobular carcinomas may metastasize as single cells and may not form cohesive clusters. If more than 200 tumor cells are present in a node cross section, then the category of micrometastasis is recommended. (C) Isolated tumor cells. A dispersed pattern of lobular carcinoma with fewer than 200 cells is detected by cytokeratin immunohistochemistry. (D) Macrometastasis with extranodal extension. This metastasis is classified as a macrometastasis based on the size of cluster (>2 mm). Extranodal extension, an area of invasion outside the lymph node capsule (arrow), is noted.
