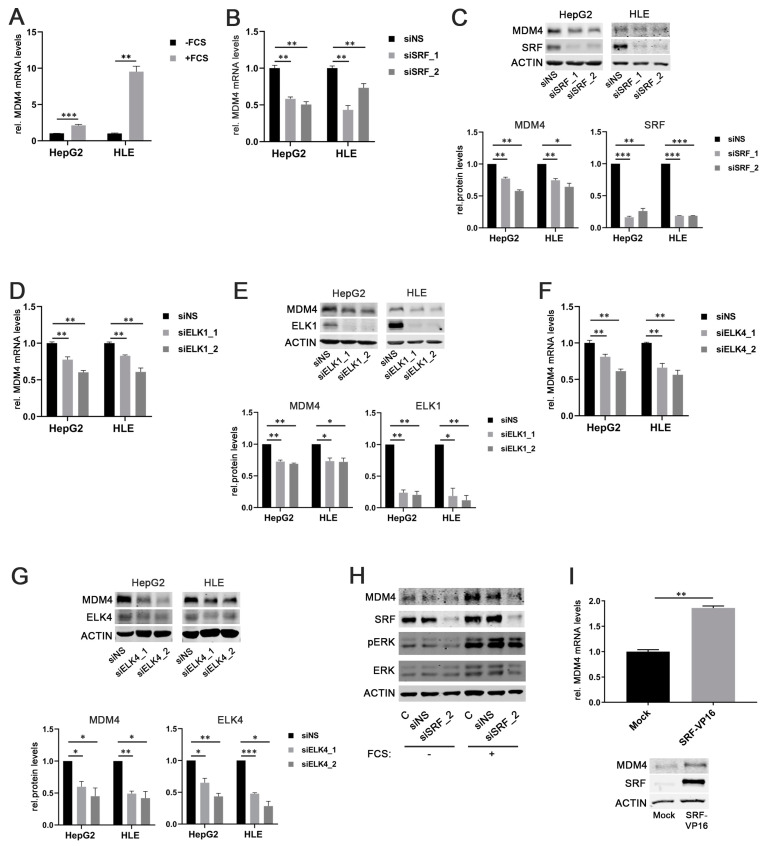
Figure 2.
SRF, ELK1, and ELK4 regulate MDM4 expression in HCC cell lines. (A) Increased MDM4 mRNA levels in HepG2 and HLE cell lines following fetal calf serum (FCS) stimulation compared to starved control cells. (B) MDM4 mRNA and (C) protein levels following siRNA-mediated knockdown of SRF compared to control cells transfected with a scrambled, nonsense siRNA (siNS) in HepG2 and HLE cells. (D) MDM4 mRNA and (E) protein levels following siRNA-mediated knockdown of ELK1 compared to control cells transfected with a scrambled, nonsense siRNA (siNS) in HepG2 and HLE cells. (F) MDM4 mRNA and (G) protein levels following siRNA-mediated knockdown of ELK4 compared to control cells transfected with a scrambled, nonsense siRNA (siNS) in HepG2 and HLE cells. (H) siRNA-mediated knockdown of SRF (siSRF_2) prevents FCS-stimulated MDM4 protein upregulation. (I) MDM4 mRNA and protein expression 48 h following transfection of HuH7 cells with an SRF-VP16 expression vector compared to mock transfected control cells. Original western blots are shown in Figures S7 and S8. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Mann–Whitney U test: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. Abbreviations: siNS—scrambled, nonsense siRNA; siSRF_1/_2, siELK1_1/_2, siELK4_1/_2—siRNA 1 and 2 specifically targeting SRF, ELK1, and ELK4, respectively.