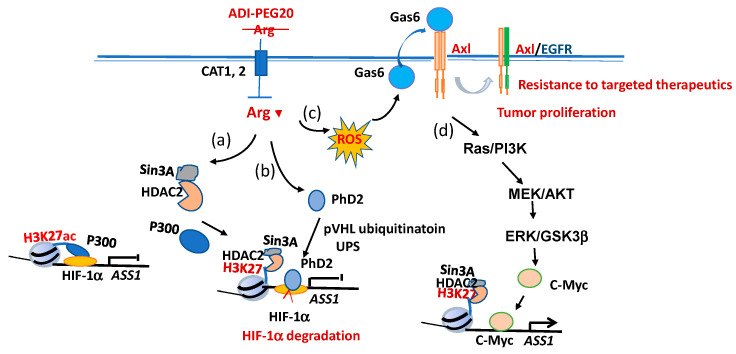
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of argininosuccinate synthetase (ASS1) induction by Arg starvation. Arg-depleting recombinant proteins such as pegylated arginine deiminase (ADI-PEG20) digests extracellular Arg, resulting in the depletion of intracellular Arg. (a) Before ADI-PEG20 treatment, ASS1 is silenced by HIF-1α binding to its promoter due to the association of histone acetyltransferase p300, which acetylates H3K14ac and H3K27ac (for simplicity, only H3K27ac is indicated). ADI-PEG20 treatment prompts P300 dissociation from the promoter, allowing histone deacetylase HDAC2 and co-factor Sin3A to deaceacetylate histone H3K27ac and H3K14ac. (b) Propyl hydroxylase (PhD2)–pVHL ubiquitine–proteosomal system moves in to the ASS1 promoter and destroys HIF-1α (see reference 54). (c) In the meantime, Arg deprivation generates reactive oxygen species (ROS), which triggers gas6 externalization to interact with the Axl receptor. (d) Axl activates the signal transduction involving Ras/PI3K, MEK/AKT and ERK/GSK3b resulting in the stabilization of c-Myc, which is a positive transcription factor to turn one ASS1 expression [55]. Then, elevated ASS1 feedbacks to suppress c-Myc and Axl signaling.