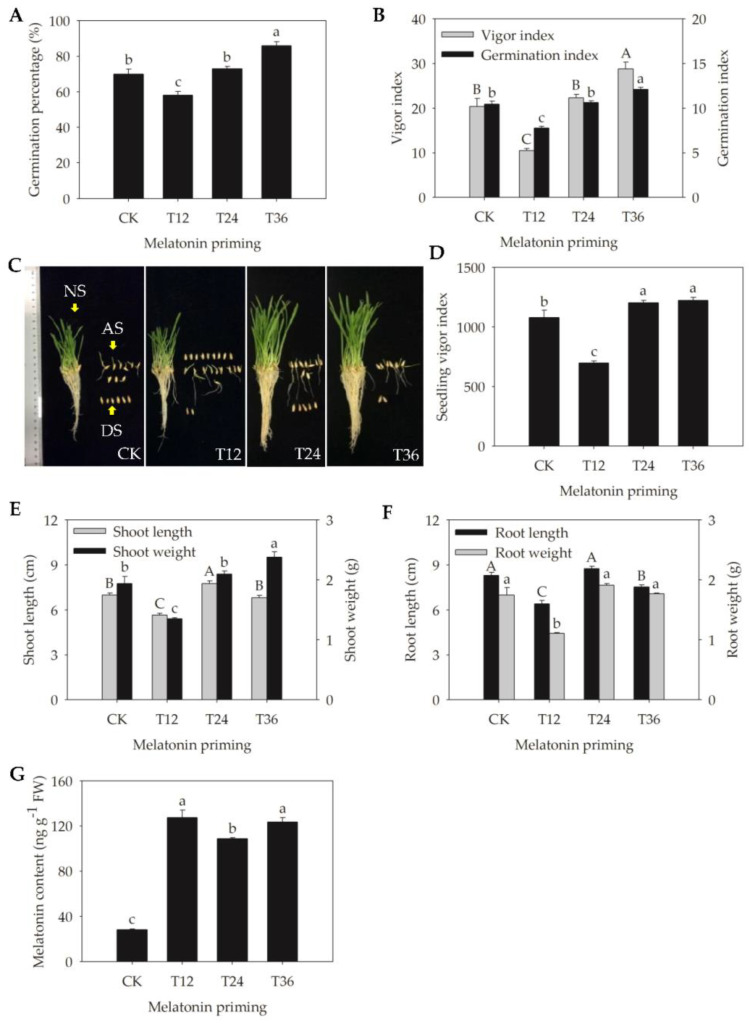
Figure 1.
Seed germinability and seedling growth status of aged oat seeds after melatonin priming. (A) Germination percentage (GP) (CK, aged seeds; T12~T36, seeds that aged and then were further primed with 10 μM of melatonin for various durations of 12, 24, and 36 h); (B) Seed vigor index (VI) and germination index (GI); (C) Seedling phenotypic characteristics on the 10th day of germination; yellow arrows showed normal seedlings (NS), abnormal seedlings (AS), and dead seeds (DS), respectively; (D) Seedling vigor index (SVI); (E) Shoot length (SL) and shoot weight (SW); (F) Root length (RL) and root weight (RW) of seedlings; and (G) Melatonin content. Values represent the means ± SE from four replicates. One-way ANOVA was adopted to perform the statistical analysis. Different letters indicated significant differences between melatonin-primed seeds and aged seeds at the 0.05 level.