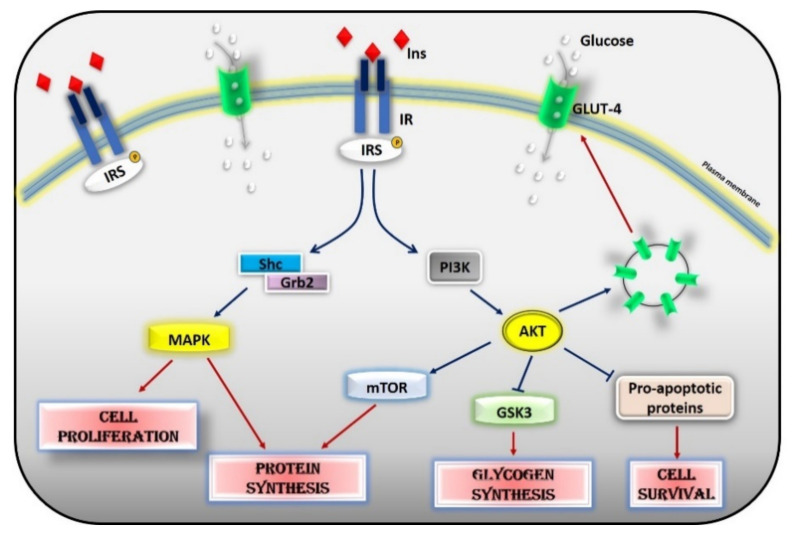
Figure 2.
Insulin signaling cascade. Insulin activates the insulin receptor, which phosphorylates IRS in tyrosine residues. IRS, in turn, activates MAPK via SHc/Grb2 and AKT via PI3K. Activated AKT induces glycogen synthesis through inhibition of GSK-3, protein synthesis via mTOR signaling, cell survival through inhibition of several pro-apoptotic agents, and the translocation of GLUT-4 to the cell membrane. Activated MAPK induces cell proliferation and protein synthesis. Abbreviations: INS = Insulin; IR = Insulin Receptor; IRS = Insulin Receptor Substrate; Shc = Src Homology 2 Domain-Containing; Grb2 = Growth factor Receptor-Bound protein 2; MAPK = Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase; PI3K = Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT = Protein kinase B; mTOR = Mammalian Target of Rapamycin; GSK3 = Glycogen synthase kinase 3; GLUT4 = Glucose Transporter type 4.