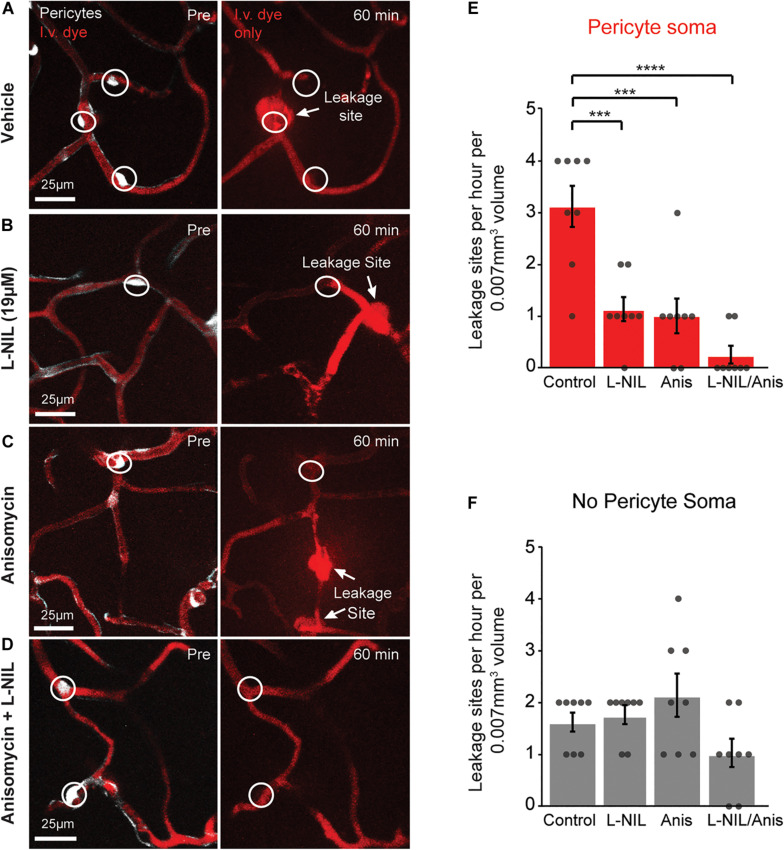
FIGURE 3.
Additive effect of L-NIL and anisomycin on pericyte-associated BBB leakage. (A–D) Representative examples of pericyte-associated BBB leakage in the vehicle group (A), and with administration of high-dose L-NIL (B), anisomycin (C), and L-NIL + anisomycin (D). (E) Effect of inhibitors on incidence of BBB leakage at pericyte somata. Pericyte soma leakage sites per hour per 0.007 mm3: 3.125 ± 0.398 (veh), 1.125 ± 0.227 (19 μM L-NIL), 1.000 ± 0.327 (anisomycin), 0.250 ± 0.164 (19 μM L-NIL + anisomycin). One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test; F(3, 28) = 17.58, ***p < 0.0001 overall, ***p = 0.0003 (vehicle vs. 19 μM L-NIL), ***p = 0.001 (vehicle vs. anisomycin), ****p < 0.0001 (vehicle vs. L-NIL + anisomycin); N = 8 mice (one region imaged per mouse) for each treatment group. Data is presented as mean ± S.E.M. (F) Effect of inhibitors on incidence of BBB leakage at non-soma locations. Non-soma leakage sites per hour per 0.007 mm3: 1.625 ± 0.183 (veh), 1.750 ± 0.164 (19 μM L-NIL), 2.125 ± 0.398 (anisomycin), 1.000 ± 0.267 (19 μM L-NIL + anisomycin). One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test; F(3, 28) = 3.015, p = 0.05 overall, non-significant; N = 8 mice (one region imaged per mouse) for each treatment group. Data is presented as mean ± SEM.