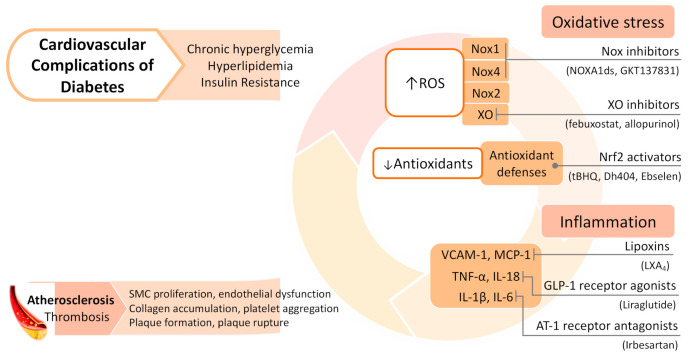
Figure 2.
Pathophysiology and therapeutic strategies of diabetes associated cardiovascular disease. AT-1, angiotensin II type 1; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide 1; IL, interleukin; MCP-1, monocyte chemotactic protein-1; Nox, NADPH oxidase; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion protein 1; XO, xanthine oxidase.