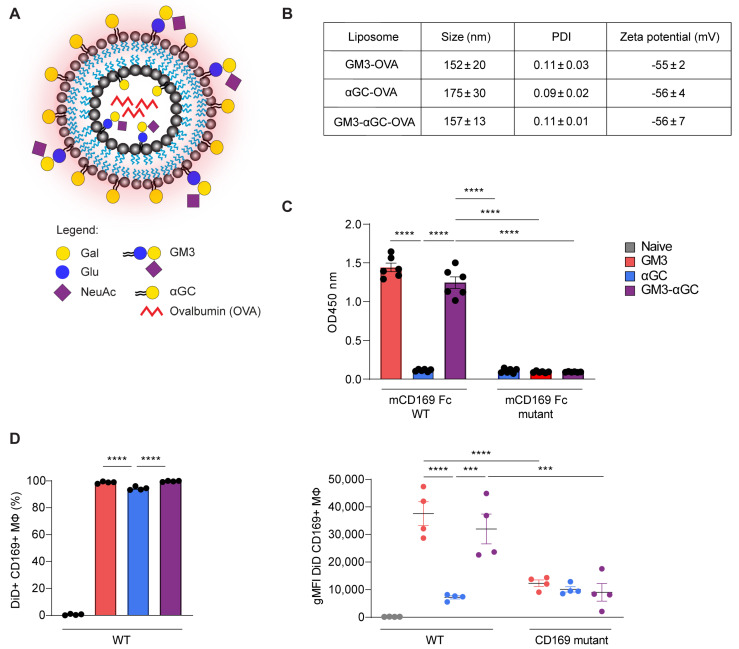
Figure 1.
Liposome characterizations and their targeting potential to CD169+ macrophages. (A) Schematic representation of OVA-containing, DiD-labelled (red glow) nanoparticles with αGC and/or GM3 incorporated into the bilayer. Gal, galactose; Glu, glucose; NeuAc, sialic acid; GM3, ganglioside GM3; αGC, alpha-galactosylceramide. (B) Liposomal size, PDI (polydispersity index) and zeta potential. The data are the mean ± SEM of three liposome batches (C) Liposome binding to mouse CD169-Fc WT or CD169-Fc mutant complexes determined by ELISA. The data are the mean ± SEM from three liposome batches measured in duplicate. (D) Liposome uptake at 2 h post immunization (p.i.) by CD169+ macrophages from WT mice illustrated by the frequency of DiD+ cells (left panel) and the DiD fluorescence signal indicated as geometric mean fluorescence intensity (gMFI) from WT and CD169 mutant mice (right panel), determined by flow cytometry. The data are the mean ± SEM from one experiment with four mice per group. Each symbol represents one mouse (one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test: *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001).