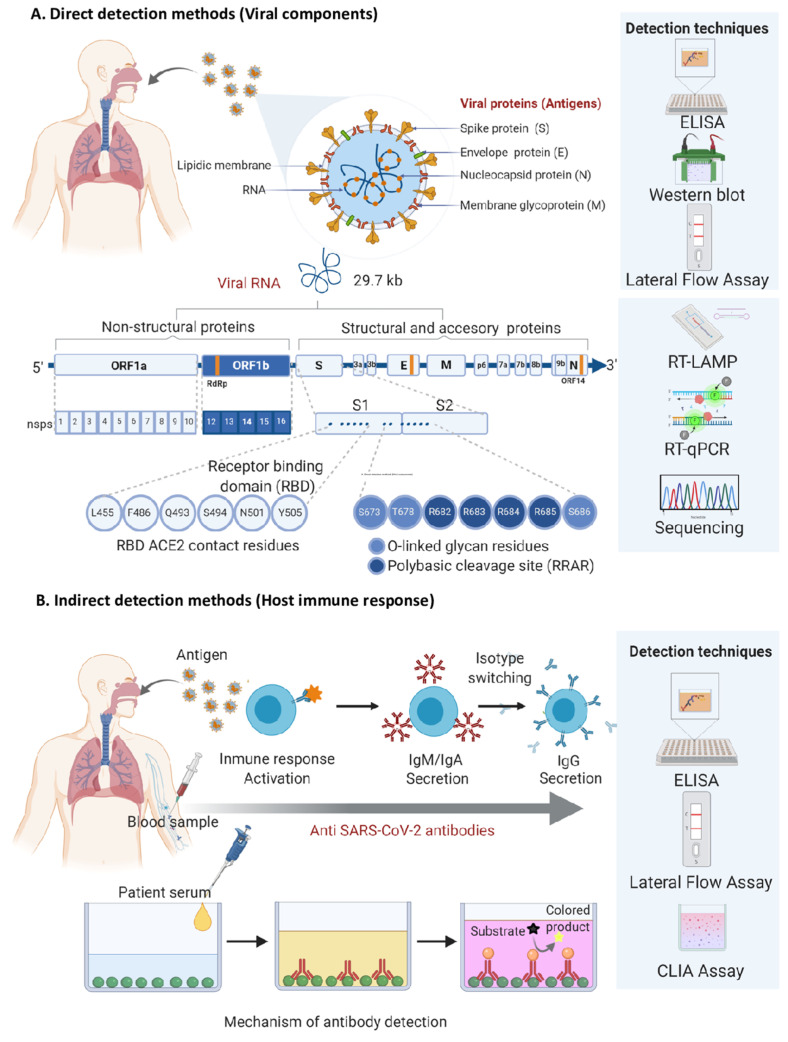
Figure 1.
Fundamental elements for the recognition of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) used in the diagnostic tests validated in Mexico. (A) Direct detection methods target viral components such as viral proteins and genome. RT-qPCR and new generation sequencing are the main techniques used for viral genome detection; while ELISA, LFA, and Western Blot are used for viral protein detection. A positive result indicates that the virus is present in the analyzed sample and may be used to detect currently infected patients. The RT-LAMP technology also focuses on the detection of the viral genome, but its use in Mexico has not yet been validated. (B) Indirect detection methods are directed against anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies produced by the host´s immune cells after an infection event. This strategy uses recombinant viral proteins as bait to capture the host´s antibodies. Due to the time needed for antibody production, a positive result means that the person was infected at some point in the past, but may not be currently infected. Antibodies can be detected by LFA, ELISA, and CLIA. CLIA: Chemiluminescent immunoassay; LFA: lateral flow assay; ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; RT-qPCR: quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; RT-LAMP: reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification.