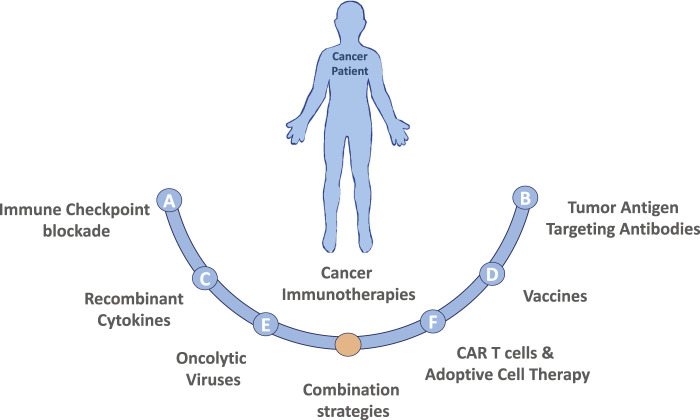
FIGURE 1.
Major types of cancer immunotherapies. (A) Immune Checkpoint blockade therapy utilizing antibodies targeting CTLA-4 or PD-1/PD-L1 pathway have demonstrated promising results in a variety of malignancies. Additionally, recent studies have identified many other immune checkpoint markers, such as LAG3, TIM3 or TIGIT that could also be targeted. (B) Tumor Antigen Targeting Antibodies are laboratory generated, designed to target specific tumor antigens, usually conjugated with a specific drug. Currently the development of polyspecific antibodies (bi- and tri-specific antibodies) has the advantages by targeting multiple tumor antigens, to more precisely and effectively eradicate cancer cells. (C) Recombinant Cytokines (e.g., IL-2, IL-18, IL-6, IFNγ, GM-CSF) can induce, mediate and regulate the immune response by improving antigen priming, facilitating T cell proliferation and survival or enhancing their cytolytic activity. (D) Therapeutic Vaccines made of laboratory modified cancer cells, parts of cells, or pure antigens elicit an immune response against tumor-specific or tumor-associated antigens. (E) Oncolytic viruses (OVs) in the forms of native or engineered viruses can be used to selectively target and kill cancer cells. Advancements of genetic engineering enable successful editing of viral genome of many species to augment antitumor activity and attenuate pathogenicity, but also to express specific cytokines that favor immune cell recruitment and activation or to produce co-stimulatory molecules on tumor cells to facilitate the generation of T-cell activating signals. (F) CAR T cells and Adoptive Cell Therapy (ACT) are personalized cancer strategies relying on the collection of immune cellular components from patient, expansion and/or genetically modification of those cells in vitro and injection them back to the patient to achieve a therapeutic response. Combination strategies involving the immunotherapies described above as well as combinations including both standard of care chemotherapy or radiation treatment options are also actively being tested in both preclinical models and in the clinical setting.