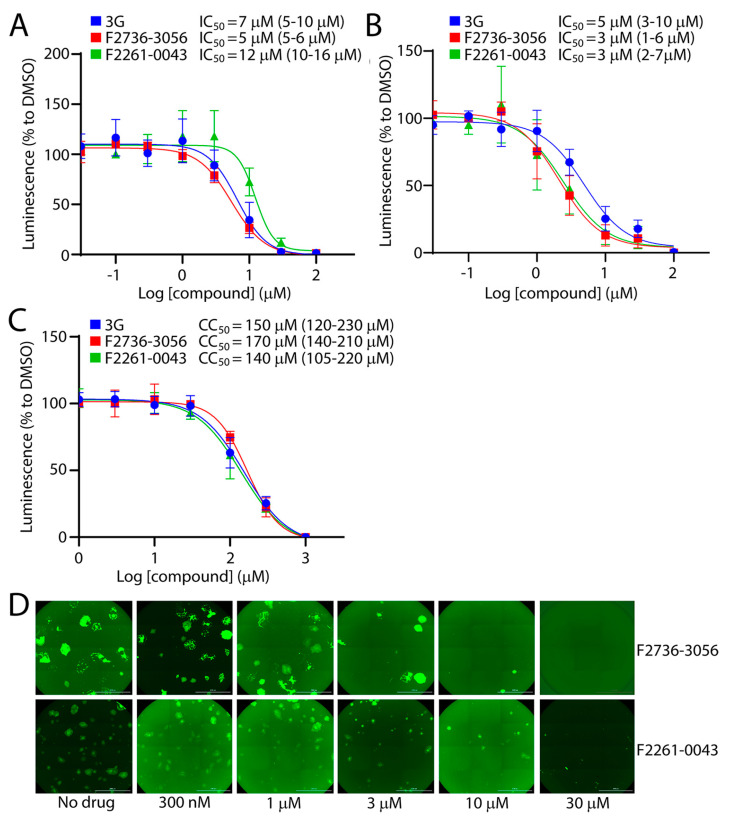
Figure 3.
Infection inhibition efficiency of F2261-0043 and F2736-3056. (A) IC50 measurement of compounds against the attenuated OP-CDV strain. Vero-cSLAM cells were treated with increasing concentration of inhibitors (either F2261-0043, F2736-3056 or 3G) and infected with OPneon/nLucP at an MOI of 0.04. Viral replication efficiency was determined by the measurement of luminescence produced by infected cells. (B) IC50 measurement of compounds against the wild type A75/17-CDV. Vero-cSLAM cells were treated with increasing concentration of inhibitors (either F2261-0043, F2736-3056 or 3G) and infected with A75/17neon/nLucP at an MOI of 0.04. Viral replication efficiency was determined by the measurement of luminescence produced by infected cells. (C) Measurement of the cytotoxic effect of the inhibitors. Vero-cSLAM cells were treated with increasing concentration of the compound and assessed for the viability using real time Glo MT cell viability assay (Promega). (D) Assessment of the compounds’ inhibitory impact on virus-induced cytopathic effect (CPE). Microscopic images of cells infected with OPneon in the presence of increasing concentration of the compounds (F2261-0043 and F2736-3056). IC50 and CC50 concentrations were calculated through four-parameter variable slope regression modeling using GraphPad Prism. All the 95% confidence intervals are shown in parentheses. The values for each concentration of the compound were normalized to DMSO-treated cells at identical concentration. Scale bars: 2000 μm.