Figure 3. Epac1 promotes macrophage accumulation of ox-LDL.
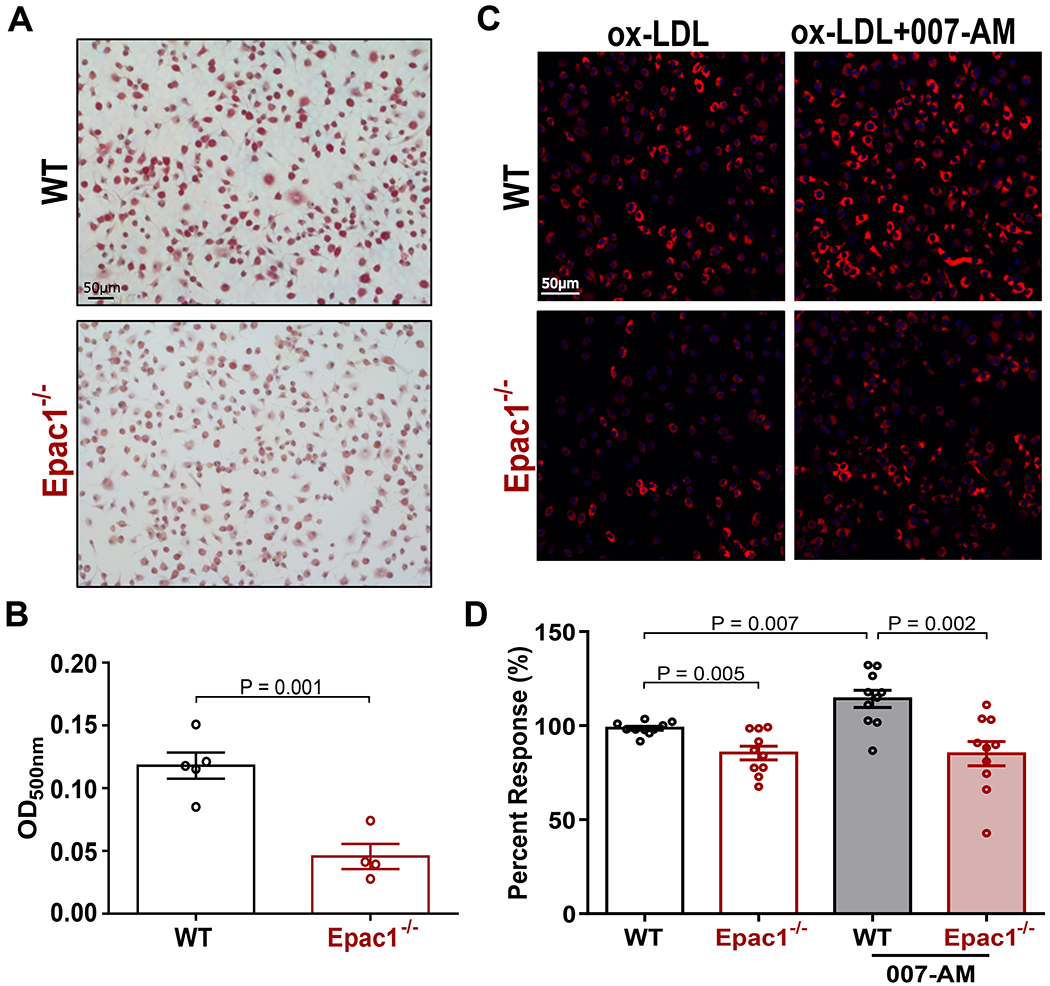
(A) Representative images of ORO stained WT and Epac1−/− foam cells (B) Quantification of ORO staining in A by methanol elution. Data are depicted as mean ± SEM (N = 5 or 4 for WT and Epac1−/−, respectively). (C) Representative fluorescence images from WT and Epac1−/− BMDMs treated with DiI-ox-LDL (10 μg/mL) for 2 h following serum starvation in the presence or absence of 007-AM (5 μM). (D) Quantification of DiI-ox-LDL fluorescence intensity in C based on automated capture of a minimum of 20 random fields of view for each genotype per well. Data are presented as mean percent response ± SEM compared to WT BMDM treated with DiI-ox-LDL alone (N = 10 BMDM cultures from independent animals for each genotype).
