Fig. 1. RP-182 induces the closed conformation of CD206.
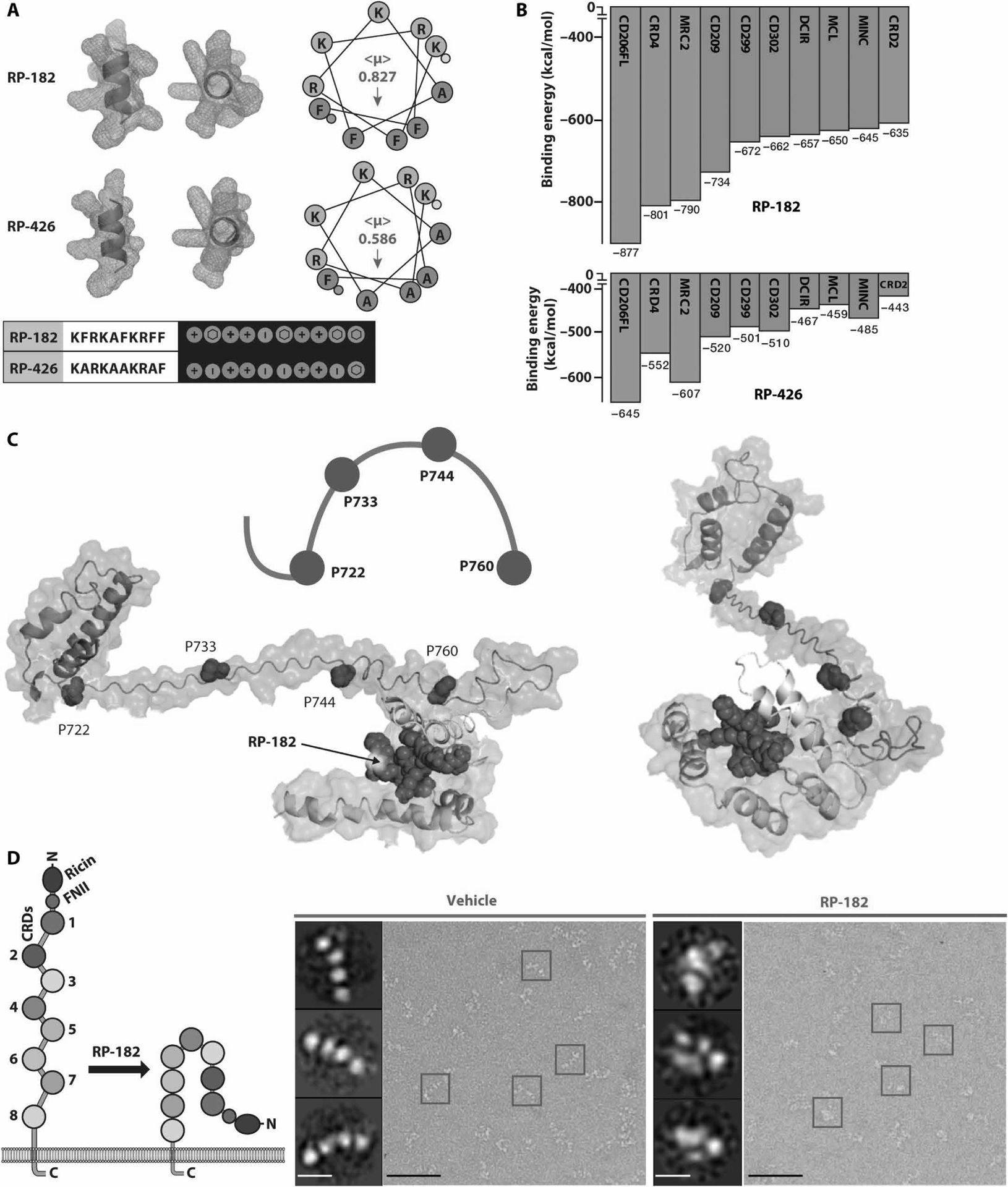
(A) Secondary α-helical structures, helical hydrophobicity wheel projections, and Molly font alignments (bottom) of RP-182 and RP-426. Amphiphilic surface topology shown in cyan (hydrophobic) and magenta (hydrophilic) colors. (<μ>), hydrophobic moment vectors; red arrows indicate strength and direction; yellow and green dots represent N and C termini. (B) Relative binding energies for the top 10 C-type lectin receptors using ClusPro. Green bars, C-type lectin class VI receptors, blue class II receptors. CRD4, carbohydrate recognition domain 4 of CD206. (C) Model of conformational bend in CRD4 and CRD5 of CD206 induced by RP-182. Hydrophobic plane of RP-182 bound to CRD5 (cyan color). (D) Negatively stained electron micrographs of CD206 proteins incubated with vehicle (blue squares) and RP-182 (red squares) and corresponding 2D single-particle images (insets); schematic of open “elongated” and “closed” conformations on left. Scale bars, 50 nm; insets, 5 nm.
