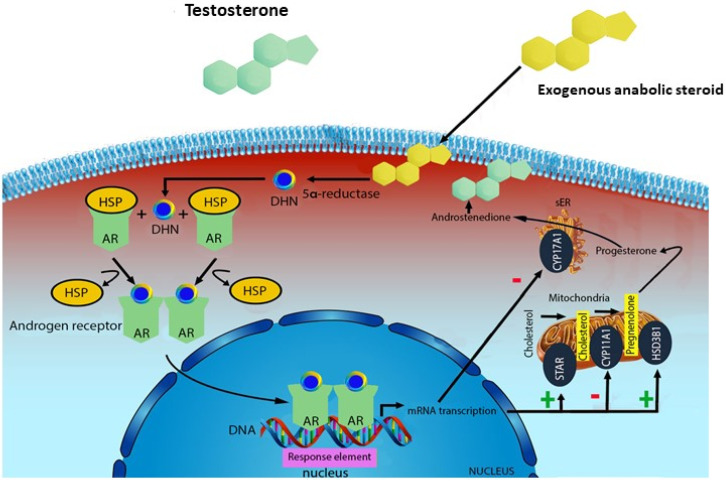
Figure 1.
Mechanism of action of exogenous anabolic steroids: an anabolic steroid is transported into the target tissue cell cytoplasm where it can either bind the androgen receptor, or be reduced by the cytoplasmic enzyme 5-alpha reductase. The N-receptor complex undergoes a structural change that allows its translocation into the cell nucleus, where it directly binds to specific nucleotide sequences of the chromosomal DNA. The produced DNA interferes with the physiological biosynthesis of testosterone.