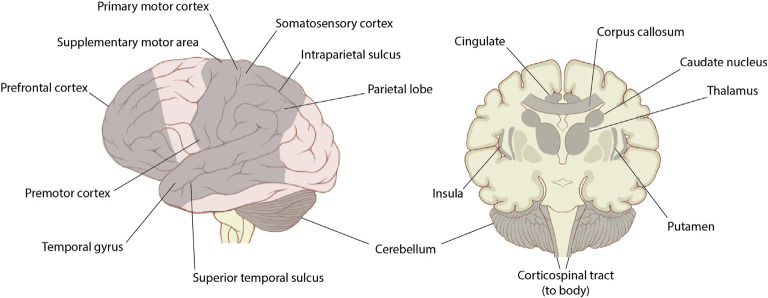
Figure 5.
Lateral view and the coronal section of the brain with regions shown to be affected by dance highlighted in gray. Previous literature has reported that dance affects the prefrontal cortex (including ventral medial PFC, medial PFC, and dorsolateral PFC), motor areas (including the primary motor cortex, supplementary motor area, and premotor cortex), somatosensory cortex, temporal areas (including superior temporal gyrus, middle temporal gyrus, and superior temporal sulcus), parietal areas (including superior parietal lobe, inferior parietal lobe, and intraparietal sulcus), cerebellum (including anterior cerebellar vermis and lateral cerebellum), cingulate (including ventral anterior cingulate cortex, ventral medial cingulate cortex, posterior cingulate, and cingulate motor area), caudate nucleus, thalamus, insula, putamen, corpus callosum, and the corticospinal tract. Image source by Patrick J. Lynch via Creative Commons.