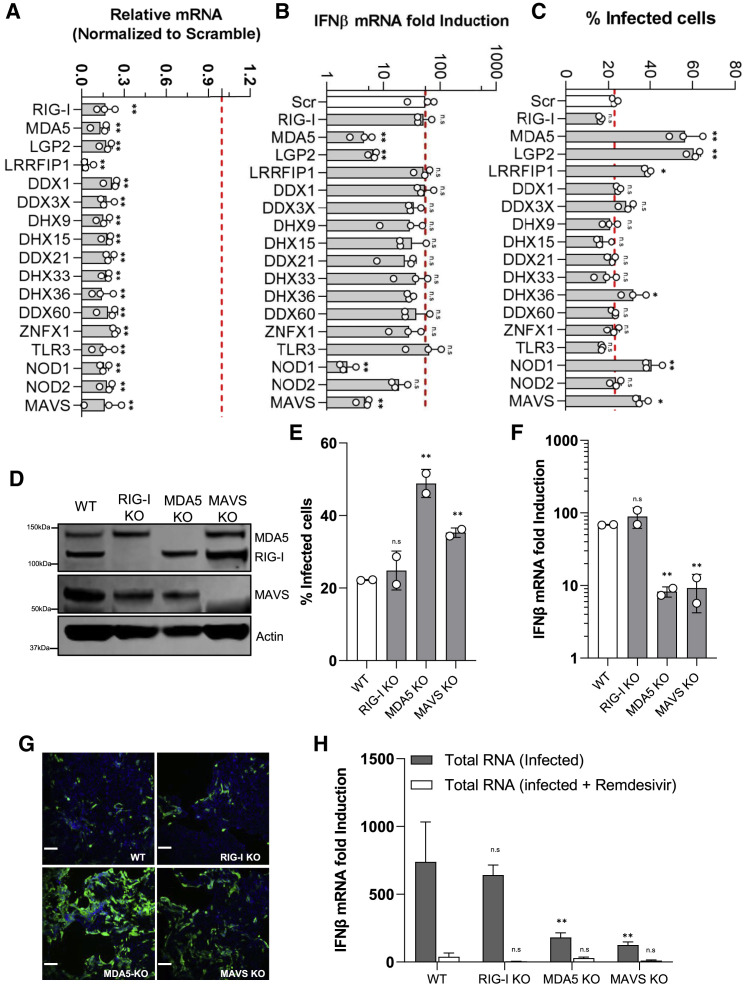
Figure 4.
MDA5/LGP2 Are the Dominant RNA Sensors Responsible for Innate Immune Induction in Calu-3 Cells Infected with SARS-CoV-2
(A) siRNA-mediated knockdown efficiency in Calu-3 cells was evaluated using qRT-PCR with specific primers.
(B) The siRNA-transfected Calu-3 cells were infected with SARS-CoV-2 with MOI = 0.125. At 48 h post-infection, the total RNA was extracted using the NucleoSpin 96 RNA extraction kit. The IFN-β mRNA was quantified by quantitative RT-PCR. Data are expressed as fold change relative to non-treated cells.
(C) The percentage of infection was calculated as the ratio between the number of infected cells stained for SARS-CoV-2 NP and the total amount of cells stained with DAPI. Data are from three independent experiments with three technical replicates.
(D) Immunoblots of parental, MDA5, RIG-I, MAVS, and β-actin in the CRISPR-knockout (KO) Calu-3 cells.
(E) The CRISPR-knockout cells were infected with SARS-CoV-2 with MOI = 0.125. At 48 h post-infection, cells were fixed, immunostained with rabbit-anti-SARS-CoV-2 NP antibody, and imaged using Celigo. The percentage of infection was calculated as the ratio between the number of infected cells stained for SARS-CoV-2 NP and the total amount of cells stained with DAPI. Data are from two independent experiments with three technical replicates.
(F) IFN-β mRNA induction in the CIRPSR-KO cells infected with SARS-CoV-2.
(G) Representative immunofluorescence images are shown.
(H) The CRISPR-KO cells were transfected with either PolyI:C (5 μg/mL) or total RNA extracted from infected cells (10 μg/mL). 8 h post-transfection, the cells were lysed to measure IFN-β mRNA production using qRT-PCR.