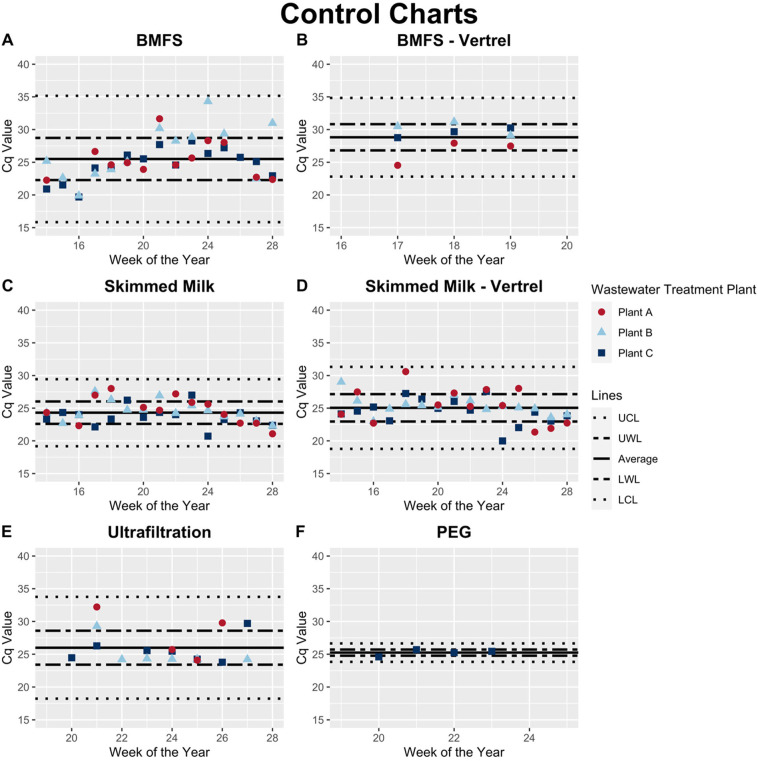
Fig. 2.
OC43 RT-qPCR control charts. Average Cq values were calculated for each method by averaging across treatment plants and time. The UWL and LWL, or upper and lower warning limits, for each method were calculated by adding or subtracting, respectively, the standard deviation from the average Cq. The UCL and LCL, or the upper and lower control limits, for each method were calculated by adding or subtracting, respectively, three times the standard deviation from the average Cq. Anything detected at or above a Cq of 40 was considered a non-detection. All samples that had non-detections by RT-qPCR in the undiluted samples reported here had detection in the 10−1 dilution. BMFS without Vertrel extraction (A) has a lower average Cq compared to BMFS with Vertrel extraction (B), but has a substantially larger range of data. Skimmed milk flocculation without Vertrel extraction (C) and with Vertrel extraction (D) have similar average Cq's, control limits, and warning limits. Ultrafiltration (E) had a similar average Cq to both skimmed milk methods, but had a larger variability in the data and fewer detections in the undiluted samples. PEG precipitation (F) had a low average Cq and variability around the mean, but only one treatment plant was tested with this method and it is therefore not directly comparable.