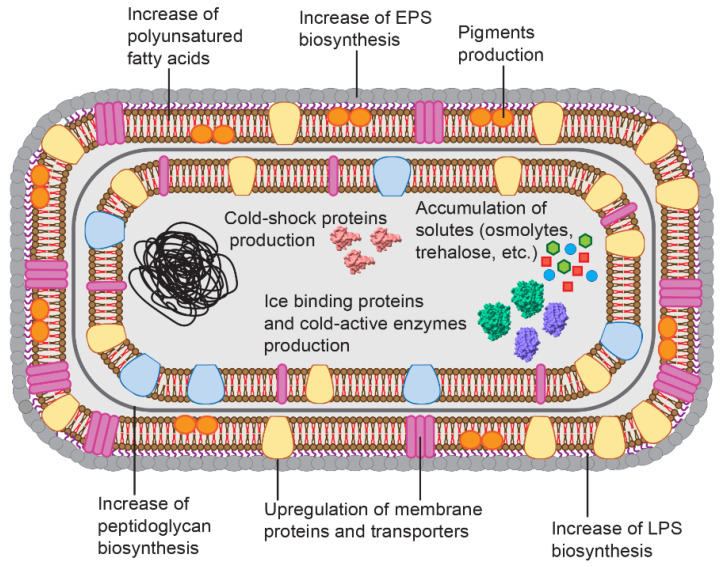
Figure 1.
Most common strategies of cold adaptation in bacteria. To survive at low temperatures, bacteria developed several strategies, including the production of cold-shock proteins, ice-binding proteins, cold-active enzymes and compatible solutes. Adaptive changes observed in the inner and outer membranes include the production of pigments (e.g., carotenoids), the upregulation of membrane proteins and transporters and the increase of the biosynthesis of polyunsaturated fatty acids, peptidoglycan, extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) and lipopolysaccharides (LPS).