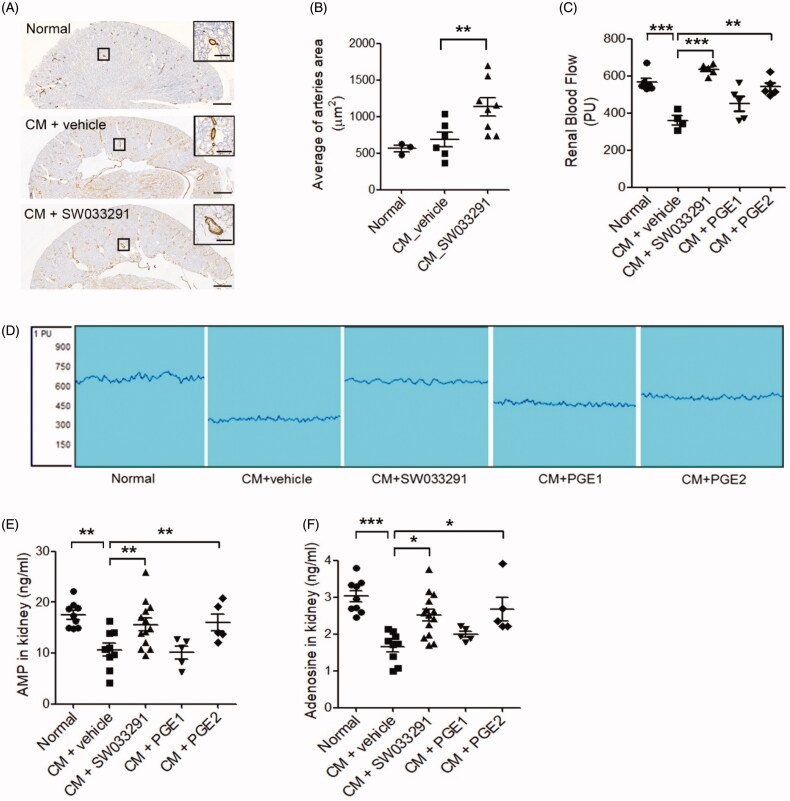
Figure 5.
15-Hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase inhibition induces renal vasodilation in the outer medulla via the adenosine monophosphate (AMP)–adenosine signaling pathway. (A) Representative images of arterioles in the outer zone of the renal medulla. Magnified images are enlargements of the outlined areas. (B) Statistical analyses of the inner arteriole area of the outer medulla. (C) Statistical analyses of renal blood flow following administration of a vehicle, SW033291 (inhibitor), prostaglandin E1 (PGE1), or PGE2 in contrast-induced acute kidney injury mice. (D) Representative images of renal blood flux measurements of the study groups. (E,F) Statistical analyses of AMP and adenosine levels in kidney tissue. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. Scale bars, 500 μm; scale bar in the enlarged image, 50 μm. CM: contrast medium.