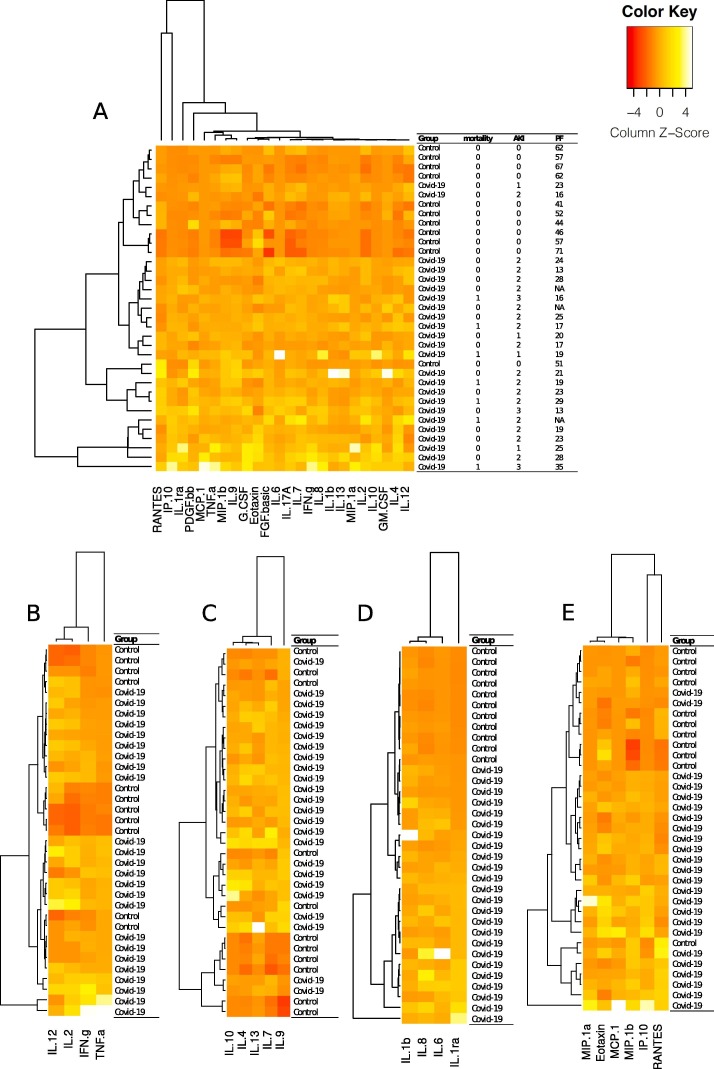
Fig. 1.
A heatmap showing hierarchical clustering of individual patients according to the detectable plasma concentration of 24 out of 27 analyzed cytokines (A). The clustering of patients in the general heatmap is largely driven by the relatively high concentrations of IP-10 and RANTES (A). The cytokines were further separated into subgroups and shown in separate heatmaps; Th1-cytokines (B), Th2-cytokines (C), Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain, Leucine rich Repeat and Pyrin domain containing Proteins (NLRP) associated cytokines (D) and chemokines (E). IL-12, IL-2, IFN γ and TNF α were categorized as Th1-cytokines. Th1 cytokines participate in cell mediated immunity, promotes inflammation and tissue damage [40]. IL-10, IL-4, IL-13, IL-7 and IL-9 were categorized as Th2-cytokines (C). Th2-cytokine expression plays a role in humoral immunity and may act anti-inflammatory [41]. NLPR-associated mediators (D) IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8 and IL-1ra take part in the innate immune response including promoting immune cell infiltration of infected tissues. Notably, these cytokines clustered the groups perfectly [42], [43]. MIP-1a, eotaxin, MCP-1, MIP-1b, IP-10 and RANTES were grouped as chemokines [44]. The color key of the calculated z-score represents a scale of −4 to 4 SD where the individual value departs from the group mean as shown in the figure.